Proteolytic Enzymes: Your Guide to Better Digestion, Inflammation, and Recovery
Discover the science behind these natural "protein-eaters," their surprising health benefits, and where to find them in foods and supplements.

Your body houses over 580 different proteolytic enzymes – microscopic protein-destroying machines that could revolutionize how you think about digestion, recovery, and inflammation. [1]
Recent 2024 clinical trials show these natural catalysts can match prescription anti-inflammatory drugs for arthritis pain while supporting everything from post-workout recovery to immune system function.
The evidence keeps mounting.
- A randomized trial with 120 participants found that multi-enzyme supplementation for just two months significantly improved quality of life scores and reduced pain severity compared to placebo. [2]
- Another 2024 study using ileostomy patients provided direct proof that enzyme blends increase nutrient absorption in the human small intestine by measurable amounts. [3]
These aren’t just laboratory “curiosities” – proteolytic enzymes represent one of the largest enzyme families in human biology, making up more than 3% of all protein-encoding genes.
Ancient cultures recognized their power centuries ago, using papaya latex for wound healing and pineapple preparations for inflammation. Modern science is finally catching up to what traditional healers knew all along.
What Are Proteolytic Enzymes?
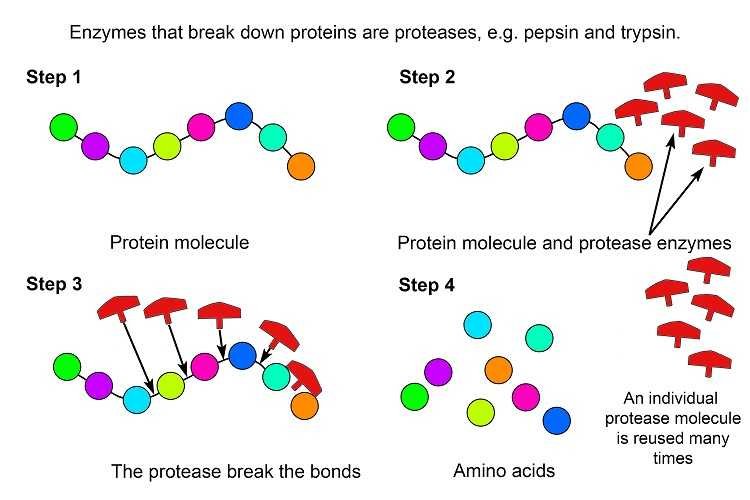
Proteolytic enzymes go by several names – proteases, proteinases, or simply “protein-eaters” – but they all do the same thing.
These biological catalysts “slice” through protein molecules like molecular scissors, breaking them down into smaller peptides and individual amino acids your body can actually use. [3]
Think of proteins as long, complex chains. Your digestive system can’t absorb these massive molecules whole.
Proteolytic enzymes accelerate protein breakdown by 10 to 13 orders of magnitude over what would happen naturally – making them among the most efficient biological catalysts on Earth.
Your body’s digestive assembly line relies on three main proteolytic enzymes: Pepsin kicks off protein digestion in your stomach’s acidic environment, working optimally at pH 1.5-2.0. Once food moves to your small intestine, the pancreas releases trypsin and chymotrypsin, which work in the alkaline environment at pH 8.0-8.5. [4]
Trypsin targets specific amino acid sequences (lysine and arginine), while chymotrypsin goes after aromatic amino acids like phenylalanine and tryptophan. [5]
According to Morgan Denhard, MS, RD from Johns Hopkins Medicine: “The pancreas is really the enzyme ‘powerhouse’ of digestion. It produces the most important digestive enzymes, which are those that break down carbohydrates, proteins and fats.” [6]
But here’s where it gets interesting – these enzymes don’t just work in your digestive tract. Research shows they can be absorbed intact into your bloodstream, where they provide systemic benefits throughout your body. [7]
Proteolytic Enzymes Health Benefits
The latest clinical evidence reveals proteolytic enzymes pack a much bigger punch than simple digestion support. Let’s break down what the research actually shows.
1. Boosts Digestion

- A groundbreaking 2024 study using ileostomy patients – people whose small intestines empty into external pouches – provided direct evidence that enzyme supplementation works. Researchers found the Elevase® enzyme blend significantly increased monosaccharide levels (glucose and fructose) after four hours, proving enhanced macromolecule digestion in the human small intestine. [8]
These enzymes reduce food viscosity by 2.75-fold, allowing your stomach to empty faster and more efficiently. [9]
For people with digestive issues, the benefits are even more dramatic.
- A randomized controlled trial with 120 participants suffering from functional dyspepsia found that two months of multi-enzyme supplementation significantly improved quality of life scores, reduced pain severity, and enhanced sleep quality – all with zero adverse effects. [10]
2. Fights Inflammation
- A 2023 meta-analysis by Leelakanok examined 54 articles across 39 studies and found bromelain (a proteolytic enzyme from pineapple) provided significant pain reduction compared to controls. The effect size was meaningful – mean difference of -0.27 on standardized pain scales. [11]
The anti-inflammatory mechanisms are surprisingly sophisticated. Proteolytic enzymes activate alpha-2-macroglobulin, a plasma protein that becomes a “cytokine magnet,” binding and inactivating inflammatory proteins throughout your body. [12]
They also break down fibrin deposits that contribute to inflammation and swelling while improving circulation by reducing blood viscosity. [13]
Dr. Luke R. Bucci, Ph.D., former Research Director at Biotics Research Corp., explains: “Proteolytic enzymes are able to reduce inflammation and speed healing of acute injuries, especially sports injuries. An extensive and favorable body of literature supports the efficacy and safety of proteolytic enzymes for these purposes.” [13]
3. Recovery gets fast-tracked

Athletes, pay attention.
- A randomized, double-blind study with 72 participants found that systematic enzyme therapy administered 72 hours before and after exhaustive exercise maintained maximal concentric strength significantly better than placebo (p=0.0332). The treated group showed favorable effects on inflammatory, metabolic, and immune biomarkers while experiencing reduced exercise-induced muscle damage. [14]
As Dr. Bucci notes: “In fact, several studies on boxers and proteolytic enzymes found 50% reductions in swelling and time to recovery when enzymes were given before, during and after bout.” [15]
But you don’t need to be a boxer to benefit. These enzymes enhance tissue regeneration by breaking down damaged proteins and cellular debris, essentially clearing the way for your body’s natural healing processes. [16]
It is worth mentioned this double-blind placebo study as well on 44 people who had ankle injuries derived from sport accidents, showed that protease (proteolytic) enzymes helped them to heal faster and stay 50% less time away from their training routines, compared to a group of people who took the placebo. [17]
4. Boosts Your Immune System
Recent 2023-2024 research reveals proteolytic enzymes support immune function through multiple pathways. They increase reactive oxygen species release from white blood cells, enhance cytokine production for cytotoxic effects against abnormal cells, and help degrade problematic immune complexes. [18]
Clinical studies on healthy volunteers showed measurable immunomodulatory effects after oral enzyme administration, with enhanced immune biomarker profiles particularly notable in exercise studies.
5. Joint Pain Finds Relief

This is where proteolytic enzymes really shine.
- A 2022 systematic review analyzing nine clinical studies found oral enzyme combinations (bromelain, trypsin, rutin) worked similarly to diclofenac – a powerful NSAID – for pain management but with fewer gastrointestinal side effects. [19] [20]
- The gold standard study came in 2015: a randomized controlled trial with 268 participants suffering from knee osteoarthritis. The enzyme combination proved as effective as diclofenac for pain relief while providing superior safety profiles and significant functional improvements. [21]
“About what might concern you here – will these enzymes work as well as my current pain medication?”
The research suggests yes, they can match NSAIDs for many people while causing fewer stomach problems.
6. Cancer Research Shows Promise
- A 2021 systematic review examined proteolytic enzyme therapy in complementary oncology, finding some evidence for reduced adverse effects from radiotherapy and chemotherapy, with potential survival benefits in certain tumor types. [22]
- Laboratory studies show bromelain exhibits anti-angiogenic effects and can interfere with cancer cell adhesion molecules. [23]
But here’s the critical caveat: Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center states that proteolytic enzymes have not been proven to prevent or treat cancer. Recent clinical trials show conflicting results, with some failing to demonstrate significant benefits. [24]
7. Increase Nutrients Absorption
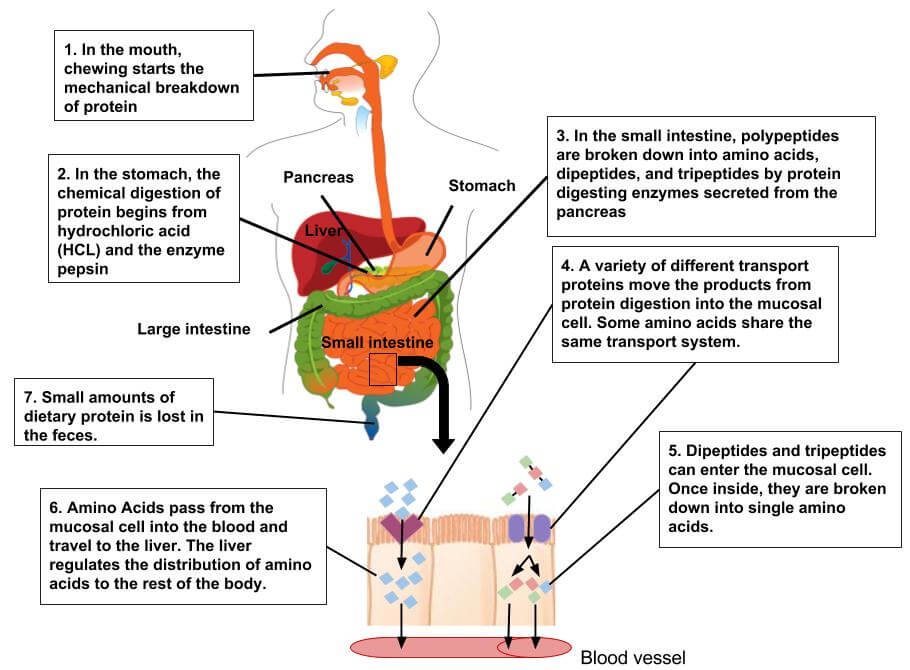
Proteolytic Enzymes help our bodies to absorb key amino acids from our foods, faster and better. For example, they help our bodies absorb up to 67% more arginine, by up to 45% more citrulline, and by 52% more tryptophan.
- Arginine is essential for blood flow and testosterone.
- Citrulline is critical for fat-burning and
- Tryptophan is essential for sleep and recovery.
They also help our bodies to absorb more of certain vitamins like folate by up to 50%. Folate – also known as vitamin B9 – is an essential vitamin to our bodies as it has the capability of producing red and white blood cells, transform carbohydrates into energy and it plays role in the production of DNA and RNA.
Protease Enzymes can also boost the absorption of the joint-protecting glucosamine by 42%. Glucosamine is a natural nutrient found in cartilage – the tissue sits between our joints. By absorbing more glucosamine from our food intake we help our joints stay in a working condition for a longer period than usual.
Additionally, proteases help your bodies absorb up to 55% more glucose from our food intake. Glucose helps the muscles of bodybuilders and athletes to recover faster. With 55% more glucose absorption, your bodies will recover in half the time after intense training.
8. Increases mental clarity and focus

Proteolytic Enzymes cleanse our guts and eliminate constipation by helping our bodies to break down food more easily and absorb nutrients faster and better.
By improving digestion and eliminating constipation our bodies have more energy to allocate for mental and cognitive functions.
Natural food sources pack serious enzyme power

Want to boost your proteolytic enzyme intake naturally? Your grocery store holds some surprisingly potent options, but preparation matters more than you might think.
Papaya delivers papain punch
Papaya contains papain, a cysteine protease that makes up a significant portion of the fruit’s protein content. Unripe papaya contains the highest concentrations – indigenous cultures have used papaya latex as a meat tenderizer for thousands of years because of papain’s powerful protein-cleaving ability.
Research confirms papain’s broad protein-cleaving specificity, capable of breaking down tough protein fibers including collagen and actomyosin. [22]
Studies demonstrate its effectiveness in improving protein digestion and reducing digestive symptoms. [23]
Pineapple’s bromelain bonanza
Fresh pineapple contains bromelain, a cysteine protease complex concentrated primarily in the core and stem.
But most people don’t know that the pineapple core contains up to 1000 GDU (Gelatin Digesting Units) per gram – far more than the flesh everyone actually eats.
Fresh pineapple juice maintains about 0.43% bromelain concentration, but here’s the kicker: canned pineapple loses 80-90% of its enzyme activity due to heat processing. [23]
Pro tip: Save that pineapple core. It’s the most valuable part for enzyme activity.
Kiwi fruit’s actinidin advantage
Green kiwifruit contains actinidin, which can make up 40-50% of the fruit’s soluble protein content. This cysteine protease remains active across a broad pH range (3.5-8.5) and stays stable up to 50°C. [24]
Studies show actinidin enhances gastric protein digestion with broader specificity than pepsin, making it particularly effective for meat, dairy, and plant proteins. [25]
SunGold kiwifruit contains only about 28% of the green variety’s enzyme activity—something to keep in mind when shopping. [26]
Ginger’s unique zingibain
Ginger contains zingibain, the only catalogued plant protease with collagenolytic activity. This enzyme shows maximum activity at 60°C with optimal pH around 6.0. [27]
Traditional Chinese cuisine uses ginger for milk coagulation (ginger milk curd) and meat tenderizing, applications that make perfect sense given zingibain’s protein-breaking capabilities. [28]
Fermented foods multiply the benefits
Fermented foods like natto, kimchi, and miso represent enzyme powerhouses created through microbial action.
Natto contains nattokinase with fibrinolytic properties, while the Bacillus subtilis fermentation produces additional proteolytic enzymes.
Kimchi’s lactic acid bacteria produce various proteases during fermentation, and miso’s Aspergillus oryzae creates extensive proteolytic enzyme systems. [29]

The fermentation process pre-digests proteins and enhances bioavailability—basically giving you a head start on digestion.
PRO TIP: Heat destroys enzyme activity. Bromelain loses 80-90% of its power during canning’s high-temperature sterilization. Papain, actinidin, and zingibain all suffer significant losses above 70°C. [30]
Light cooking under 60°C may preserve some activity, but raw consumption maintains maximum enzyme power. Refrigeration preserves activity better than room temperature storage, so keep those enzyme-rich fruits properly chilled. [31]
Proteolytic Enzyme supplements: When and How To Use Them
Sometimes food sources aren’t enough, or you need therapeutic doses for specific health issues. (Ed. note: Always consult your healthcare provider before starting any supplement regimen, especially if you take medications.)
Who might actually benefit from Proteolytic Supplements
People with digestive enzyme insufficiency represent the clearest candidates. According to Morgan Denhard from Johns Hopkins Medicine:
“About 90% of my patients with cystic fibrosis have pancreatic enzyme insufficiency. Many of them need PERT because their pancreas develops mucus and, over time, scar tissue. So it can’t release the enzymes as it should.”
Others who might benefit include older adults (natural enzyme production decreases with age), post-surgical patients, athletes seeking recovery support, and people with certain inflammatory conditions like osteoarthritis.
Common supplement types and what to look for
- Individual enzymes like bromelain (1,200-2,000 GDU per dose) or papain (3,000,000-6,000,000 PU per dose) target specific needs. Enzyme blends typically combine bromelain, papain, pancreatin, trypsin, and chymotrypsin for broader coverage.
- Plant-based sources (bromelain, papain, ficin) generally work across broader pH ranges and suit people with animal protein sensitivities. Animal-based sources (pancreatin, trypsin, chymotrypsin from pork pancreas) more closely resemble human digestive enzymes. [32]
- Quality matters enormously. Look for third-party testing from USP, NSF International, or ConsumerLab.com. Ensure labels list activity units (GDU, PU, HUT) rather than just weight – enzyme potency is measured by what they can do, not how much they weigh.
- When buying proteolytic enzyme supplements, make sure the product lists its potency in proteases. For example, MassZymes 4.0 lists on its package that it has 100.000 HUT. Many brands simply list the weight in grams or milligrams of the enzymes they have. This does not show the ”strength” of the product.
- Also, make sure that the supplement you are buying is enteric-coated. This means that each capsule or pill of the proteolytic enzyme is covered with a substance that prevents Hydrochloric acid produced by the stomach to break them down and make them ineffective. To be effective proteolytic enzymes must reach the intestine -where nutrient absorption occurs.
Finally, don’t fall for the natural or organic labels not explaining why they are labeled as such. Look at products that are reviewed third party respected agencies such us U.S. Pharmacopeia, NSF International, or ConsumerLab.com.
Timing can make or break effectiveness
- For digestive support: Take 15-20 minutes before meals or with your first bite. Verywell Health This ensures enzymes are ready when food arrives.
- For systemic effects (inflammation, recovery): Take on an empty stomach 45-60 minutes before meals or 2+ hours after eating. This prevents the enzymes from being used for food digestion, allowing systemic absorption. [33]
Best Proteolytic Enzymes Supplements
You can buy proteolytic enzymes supplements from various sources such as Amazon, iHerb or Bioptimizers. The best proteolytic enzyme in the market at the moment is MassZymes 4.0 by Bioptimizers.
Here are our top 3 recommendations
1. MassZymes 4.0 by Bioptimizers
MassZymes 4.0 is the Gold Standard of Enzyme Supplements for many reasons.
MassZymes 4.0 contains 100,000 HUTs of protease per capsule. That’s 102% more protease than the runner-up enzyme supplement currently in the market.
According to MassZyme’s founders, they literally looked at every enzyme label they could find and made their enzyme formulation better.
PRO TIP: Use discount code FDN10 at checkout for 10% OFF your order.
2. Doctor’s Best Proteolytic enzymes
Another great choice is the proteolytic supplements from Doctor’s Best. Doctor’s Best Proteolytic enzymes supplement helps support healthy digestion of proteins.
It is a potent formulation containing a broad spectrum of proteolytic enzymes (proteases) including serrapeptase, a protease derived from the silkworm.
This formulation helps break down proteins into peptides and amino acids for absorption and supports joint health, muscle health, and healthy immune function.
It is gluten free, vegetarian, and non-GMO.
PRO TIP: Shop this supplement from iHerb and use discount code GIX3955 for 10% off your order.
Wonder Laboratories Proteolytic Enzymes

Our final recommendation comes from Wonder Laboratories. Wonder Laboratories Proteolytic Enzymes are a blend of enzymes that help to support proper digestion. The formula includes bromelain, papain, pancreatin, and trypsin, all of which are essential for breaking down proteins.
This blend helps to support the body’s natural digestive process and can help to reduce inflammation.
Wonder Laboratories Proteolytic Enzymes are also standardized to ensure potency and quality.
The formula is gluten-free and dairy-free, making it a great choice for those with dietary restrictions. The tablets are easy to swallow and can be taken with or without food.
Safety, side effects, and interactions
Proteolytic enzymes are generally well-tolerated, but a few important considerations can keep you safe. In general though common side effects stay mild and most people experience no issues.
- Mild gastrointestinal upset, bloating, or gas represent the most common complaints, especially at higher doses. Some people develop allergic reactions, particularly to bromelain from pineapple sources. [34] Rarely, skin irritation can occur if capsules break open in your mouth – swallow them whole with plenty of water.
- Blood-thinning interactions – Proteolytic enzymes may enhance the effects of anticoagulant medications like warfarin, heparin, or clopidogrel. If you take blood thinners, avoid proteolytic enzyme supplements or use them only under medical supervision with frequent INR monitoring. [35]
Who should be extra cautious
- Pregnancy and breastfeeding: Insufficient safety data means avoidance is the smart choice.
- Upcoming surgery: Discontinue supplements two weeks before any scheduled procedure due to bleeding risk.
- Active gastrointestinal bleeding or severe bleeding disorders: Absolute contraindications.
- Peptic ulcers: May worsen symptoms in some people.
As Dr. Cindy M. Howard notes:
“Proteolytic enzymes can be commonly overlooked when prescribing nutrients, yet their value is enormous,” but she emphasizes the importance of proper medical evaluation first. [36]
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some FAQs we get asked by our readers. If you want to ask something feel free to contact us here.
Bottom Line
Proteolytic enzymes offer legitimate, science-backed benefits for digestion, inflammation, and recovery. The clinical evidence supports their use for specific health conditions, with safety profiles that often surpass conventional alternatives.
These enzymes work best as part of a comprehensive approach. As Morgan Denhard from Johns Hopkins emphasizes:
Overall, a healthy person really doesn’t need to take digestive enzyme supplements. The best digestive enzymes are the ones our bodies make naturally, and they work best when you eat a whole food diet.” [37]
Focus first on enzyme-rich whole foods—fresh pineapple (don’t skip the core), papaya, kiwi, ginger, and fermented foods. Raw preparation preserves maximum activity. Consider supplements as targeted tools for specific health goals or conditions rather than general health insurance.
The research is solid, the safety profile is good, and the potential benefits are real. Whether you’re dealing with digestive issues, seeking natural inflammation relief, or looking to optimize recovery, proteolytic enzymes deserve a place in your health toolkit.