What is Valine: Benefits, Deficiency, Dietary Sources

In this article, we will be diving into the world of amino acids and exploring the specific function and importance of one of the essential amino acids, Valine.
As a branched-chain amino acid, Valine plays a crucial role in muscle metabolism and overall health.
We will be discussing its chemical structure, metabolism, physiological role, dietary sources and possible deficiency. By the end of this article, you will have a comprehensive understanding of what Valine is and how it contributes to the human body’s functioning.
What is Valine?
Valine is an essential amino acid, meaning that it cannot be produced by the human body and must be obtained through diet. It is classified as a branched-chain amino acid (BCAA), along with leucine and isoleucine.
Valine plays an important role in the human body, particularly in muscle metabolism. It helps to promote muscle growth and repair, and also helps to maintain proper nitrogen balance in the body.
In addition to its role in muscle metabolism, valine may also have a role in promoting healthy energy levels and regulating blood sugar levels. It also plays a role in the production of enzymes and hormones in the body.
It’s considered a non-polar amino acid, which means it is hydrophobic and does not dissolve in water.
Valine Chemical structure
Valine is made up of a carbon (C) skeleton and contains an amino group (-NH2), a carboxyl group (-COOH), and a side chain methyl group (-CH3). The chemical formula for valine is C5H11NO2.
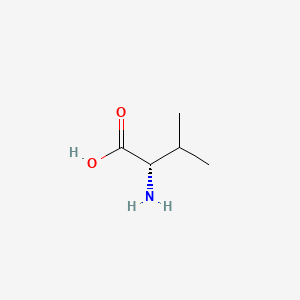
All amino acids have a common structure, which is a central carbon atom (alpha carbon) that is bonded to a carboxyl group, an amino group, and a side chain group, which differs among the 20 different amino acids. The side chain group of valine is -CH3, which is a methyl group.
Valine differs from other amino acids in its side chain group. For example, Leucine, another BCAA has a branched side chain with C6H13NO2, whereas isoleucine has a branched side chain with C6H13NO2.
These side chains give each amino acid different properties, such as solubility, polarity and acidity, which affect their behavior and function in the body.
KEY TAKEAWAY
Valine is a building block of protein, composed of a common backbone and a side chain that sets it apart from the other amino acids. This side chain gives valine unique chemical properties that affect how it interacts with other molecules in the body and how it functions in the body.
How Valine is metabolized in the body?
Valine is metabolized in the body through a process called catabolism, which is the breakdown of larger molecules into smaller ones. In the case of valine, it is broken down into smaller molecules called acetyl-CoA and pyruvate. These molecules can then be used in various metabolic pathways to produce energy or other important molecules.
Valine biosynthesis is the process by which valine is synthesized from other molecules in the body. In humans, valine biosynthesis occurs primarily in the liver, and it is synthesized from pyruvate, which is a molecule that is produced during the metabolism of carbohydrates. The process of valine biosynthesis is complex and involves several enzymatic reactions.
Valine catabolism starts in the muscle cells, where it is converted to a molecule called alpha-ketoisocaproate (KIC). KIC is then transported to the liver, where it is converted to another molecule called leucine. Leucine can then be used to produce energy or other important molecules.
KEY TAKEAWAY
Valine metabolism in the body includes both its breakdown and synthesis through catabolism and biosynthesis respectively. These processes are essential for the production of energy and other important molecules in the body, and also for maintaining proper nitrogen balance.
Valine Benefits
Valine has a number of benefits for the human body. Here are some of the key benefits of Valine:
KEY TAKEAWAY
Valine plays a crucial role in muscle metabolism, maintaining proper nitrogen balance, energy production and production of enzymes and hormones. These benefits make it an important nutrient for overall health and well-being.
Valine Deficiency
Although a deficiency of valine is rare, in certain situations, such as severe malnutrition or certain inherited metabolic disorders, a deficiency of valine may occur. For most people, a balanced diet that includes a variety of protein-rich foods should provide enough valine to meet the body’s needs
When a deficiency of valine occurs, it can have a number of effects on the body.
KEY TAKEAWAY
Deficiency of valine is rare but can occur and it can lead to muscle wasting, nitrogen imbalance, poor wound healing, decreased immune function, fatigue and in severe cases neurological symptoms. A balanced diet that includes a variety of protein-rich foods can provide enough valine to meet the body’s needs.
Dietary Sources
There are many dietary sources of valine, some of the best sources include:
- Meat, poultry, and fish: These animal-based protein sources are rich in valine and other essential amino acids.
- Dairy products: Milk, cheese, and yogurt are also good sources of valine.
- Legumes: Beans, lentils, and peas are good plant-based sources of valine.
- Eggs: Eggs are a good source of valine, and also provide other essential amino acids.
- Whole grains: Whole grains like quinoa, barley, and oats are also good sources of valine.

The amount of valine required by the body depends on various factors such as age, sex, weight and activity level.
The dietary reference intake (DRI) for valine is about 12-14 mg/kg body weight/day for adults. Therefore, a person who weighs 150 lbs (68 kg) would require about 864 – 952 mg of valine per day.
KEY TAKEAWAY
Valine can be obtained from a variety of dietary sources such as meat, poultry, fish, dairy products, legumes, eggs, and whole grains. The amount of valine required by the body depends on various factors and it’s best to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the specific dietary needs for an individual.
Valine in sports nutrition
Valine is commonly used in sports nutrition to support muscle growth and repair. BCAAs are popular among athletes and bodybuilders because they can help to reduce muscle breakdown and promote muscle growth during intense exercise.

Valine helps to improve endurance, reduce fatigue and enhance cognitive function, which is particularly beneficial for athletes and bodybuilders who are looking to increase the intensity of their training.
Additionally, valine has been shown to help reduce soreness and muscle damage after intense exercise, which can speed up recovery time and allow athletes to return to training more quickly.
KEY TAKEAWAY
Valine is commonly used in sports nutrition to support muscle recovery and growth, reduce fatigue, and enhance cognitive function, which can help athletes to achieve their performance goals.
Bottom Line
In conclusion, Valine is an essential amino acid that plays a crucial role in muscle metabolism and overall health.
As a branched-chain amino acid, it helps to promote muscle growth and repair, and also helps to maintain proper nitrogen balance in the body. Additionally, valine may also have a role in promoting healthy energy levels and regulating blood sugar levels, and plays a role in the production of enzymes and hormones in the body.
Valine is metabolized in the body through a process called catabolism, which is the breakdown of larger molecules into smaller ones.
This article provided an overview of the chemical structure, metabolism, physiological role, dietary sources and possible deficiency of Valine, providing a comprehensive understanding of what Valine is and how it contributes to the human body’s functioning.
