What is Asparagine: Benefits, Side Effects, Foods, Science

In this article, we will take a closer look at what is asparagine, what are its benefits, its potential side effects, foods that are high in asparagine and other important information. so you can make informed decisions about your diet and overall health.
What is Asparagine?
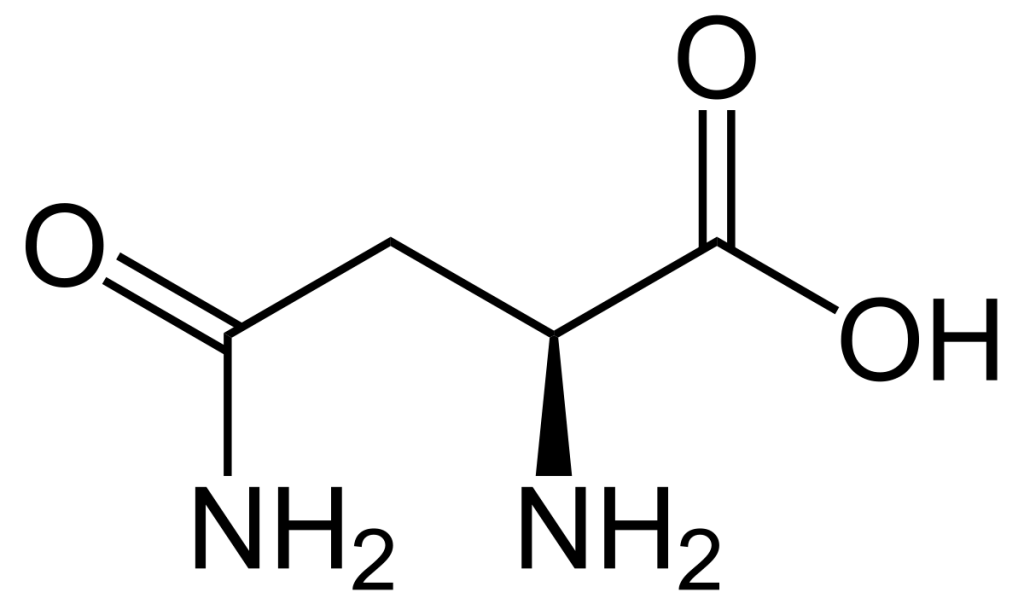
Asparagine is one of the 20 most common amino acids found in nature. It is a polar, neutral, and hydrophilic amino acid. It was named after the vegetable asparagus, which contains relatively high levels of this amino acid.
It’s an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an amino group (-NH2), a carboxyl group (-COOH), and a side chain amide group (-CONH2), making it a non-essential amino acid. It is synthesized from aspartic acid using transamination.
Asparagine is found in many different types of food. It is found in high concentrations in dairy products, beef, poultry, fish, eggs, and many vegetables.
It is considered a non-essential amino acid because the body can produce it on its own, but it is still important for various bodily functions. In the body, asparagine is used to make proteins, and it also plays a role in the formation of DNA and RNA.
Additionally, asparagine is important for the healthy functioning of the brain and nervous system, and it helps to support the immune system. It is also commonly used in the food industry as a flavoring agent and a source of nitrogen.
KEY TAKEAWAY
Asparagine is an important compound for our body, it plays various important roles in many bodily functions. It is also a common component in many food products, adding flavor and helping to support the overall health of the body.
| Formula | C4H8N2O3 |
| Molar mass | 132.12 g/mol |
| Melting point | 235 °C |
| Boiling point | 320.6 °C |
| ChemSpider ID | 231 |
| ChemSpider | 6031 |
| Solubility | soluble in acids, bases, negligible in methanol, ethanol, ether, benzene |
Asparagine Benefits
Asparagine is an amino acid that has many benefits to the human body. Here are a few examples:
- Helps in the formation of proteins: Asparagine is an essential component in the formation of proteins. As it is widely known, proteins are essential for the growth, repair, and maintenance of cells and tissues. [1]
- Supports brain and nervous system function: Asparagine plays a role in the formation of neurotransmitters, which are chemicals that help transmit signals in the brain and nervous system.
- Helps to support the immune system: Asparagine is important for the production of white blood cells, which help to fight off infection and disease – making it an important amino-adic for the overall health of the immune system.. [2]
- Helps in the formation of DNA and RNA: Asparagine is important in the formation of DNA and RNA. DNA and RNA are essential for the replication of cells and the transmission of genetic information. [3]
- Helps in the formation of other amino acids: Asparagine is also used in the formation of other amino acids, such as aspartic acid and glutamine. These amino acids also play important roles in the body, such as in the formation of proteins and in the regulation of blood sugar levels. [4]
- Helps in the digestion and absorption of food: Asparagine is a neutral and hydrophilic amino acid, which help to keep the pH balance of the stomach, and it’s also a common component in many enzymes that help in the digestion and absorption of food. [5]
Asparagine Deficiency
Since asparagine is a non-essential amino acid (which means that the body can produce it on its own), deficiency is rare. However, some people may have a deficiency in asparagine due to certain medical conditions or treatments.
Some common symptoms of asparagine deficiency include:
Fatigue: Not getting enough asparagine can cause your body to lose energy and weaken your muscles, which can lead to feeling tired and worn out. Asparagine helps with making proteins and neurotransmitters, which are important for having enough energy and keeping your muscles working right.
Impaired immune system: As I mentioned earlier, asparagine is important for the production of white blood cells, which help to fight off infection and disease. A deficiency in asparagine can lead to an impaired immune system and increased susceptibility to infections.
Slow wound healing: Asparagine is important in the formation of proteins, which are essential for the growth, repair, and maintenance of cells and tissues – which translates to slow wound healing.
Depression and anxiety: Asparagine plays a role in the formation of neurotransmitters – chemicals that help transmit signals in the brain and nervous system. Asparagine deficiency leads to bad signal transmition to the brain and nervous system, which can cause depression and anxiety.
Digestive issues: Asparagine is a neutral and hydrophilic amino acid, which is also a common component in many enzymes that help in the digestion and absorption of food. A deficiency in asparagine can lead to digestive issues such as stomach pain, bloating, gas, and diarrhea.
NOTE
Asparagine deficiency is a very rare condition, and it’s hard to diagnose without a blood test.
Asparagine Overdose
Consuming large amounts of asparagine can lead to an overdose – however, it’s important to note that asparagine overdose is considered to be very rare, because the body has the ability to remove any excess asparagine from its system.
Foods High in Asparagine
Foods that are high in asparagine include dairy products, beef, poultry, fish, eggs, and many vegetables such as asparagus, potatoes, legumes, nuts, seeds, soy, and whole grains. Here’s a list with the top 10 foods high in asparagine.
| Food | Asparagine (mg/100g) |
|---|---|
| Asparagus | 980 mg |
| Potatoes | 320 mg |
| Soy | 300 mg |
| Peas | 280 mg |
| Beef | 220 mg |
| Poultry | 210 mg |
| Fish | 200 mg |
| Eggs | 190 mg |
| Nuts | 180 mg |
| Dairy Products | 170 mg |
Frequently Asked Questions About Asparagine
Bottom Line
The bottom line is that asparagine is a non-essential amino acid that plays an important role in many functions of the body.
For example, it is important for the formation of proteins, the healthy function of the brain and nervous system, and the support of the immune system.
Asparagine is found in a variety of foods, particularly in asparagus, potatoes, legumes, nuts, seeds, soy, and whole grains.
Deficiency as well as overdose is rare because our body removes excess asparagine from its system.
When it comes to asparagine’s relation to cancer, more research is still needed to understand their relationship and more studies are needed to confirm the findings.
