10 Science-Backed Green Tea Health Benefits You Need to Know About
Unlock the secrets of this powerful beverage and learn how to harness its full potential for a healthier life

Every day, over 3.7 billion cups of tea are consumed worldwide, with green tea accounting for 20% of global tea consumption [1]. This ancient beverage, first discovered in China over 4,000 years ago, has become one of the most studied drinks in modern science.
Green tea comes from the Camellia sinensis plant, the same source as black and white tea. The key difference: minimal processing preserves its powerful compounds. While black tea undergoes fermentation that changes its chemical structure, green tea leaves are quickly steamed or pan-fired after harvest. This simple difference creates a completely different health profile.
This guide breaks down exactly what science says about green tea’s health benefits. You’ll learn which compounds deliver results, how much you need to drink, and the best ways to prepare it for maximum benefit.
What Makes Green Tea So Healthy? A Look at the Science
Green tea contains over 200 health-promoting substances. Four stand out as the heavy hitters:
Catechins, particularly EGCG = epigallocatechin gallate, the most abundant and potent antioxidant in green tea. One cup contains 50-90mg of EGCG [2]. These molecules neutralize free radicals, unstable atoms that damage cells and accelerate aging. Research shows EGCG crosses the blood-brain barrier and protects neurons from damage caused by oxidation [3].
L-theanine, an amino acid found almost exclusively in tea plants. A typical cup contains 25-60mg. This compound promotes alpha brain waves, the same waves that occur during meditation. When combined with caffeine, L-theanine creates alert calmness without jitters [4].
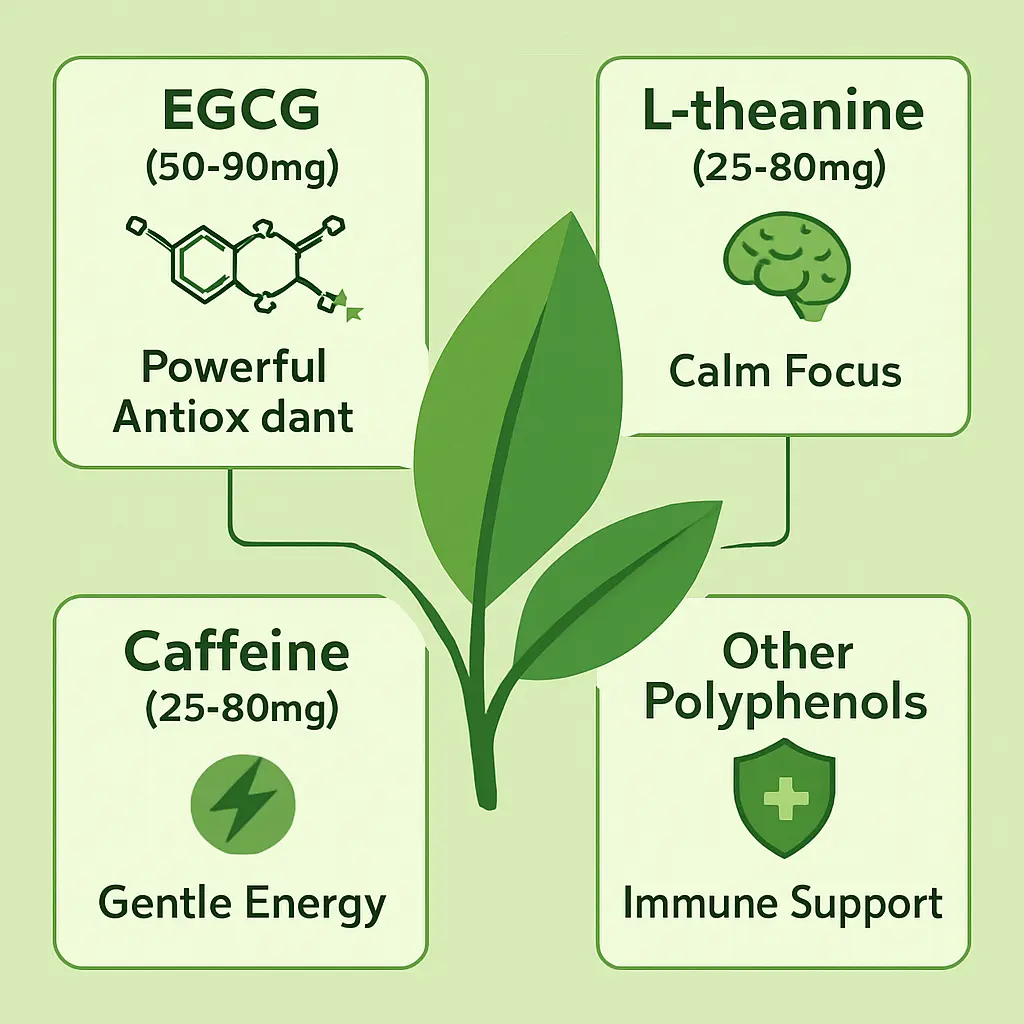
Caffeine provides 25-50mg per cup, about half the amount in coffee. This moderate dose enhances focus without causing anxiety or crashes. The slower absorption rate, thanks to L-theanine, extends the energy boost over 4-6 hours.
Additional polyphenols include theaflavins, tannins, and flavonoids. These compounds work together, creating combined effects stronger than any single component alone.
“But doesn’t processing affect these compounds?”
Yes, it does. Fresh leaves contain the highest levels. Steaming preserves more catechins than pan-firing. Storage time matters too. Green tea loses about 20% of its catechins after six months at room temperature [5].
The Top 10 Science-Backed Health Benefits of Green Tea

1. Boosts Brain Function and Protects Against Neurodegenerative Diseases
Your brain loves green tea. The combination of L-theanine and caffeine improves reaction time, memory recall, and attention span within 30 minutes of consumption [6].
A 2017 study tracked 490 Japanese adults over 60 years old. Those who drank 2+ cups daily showed significantly better cognitive performance compared to non-drinkers [7]. Brain scans revealed better connectivity between regions controlling memory and executive function.
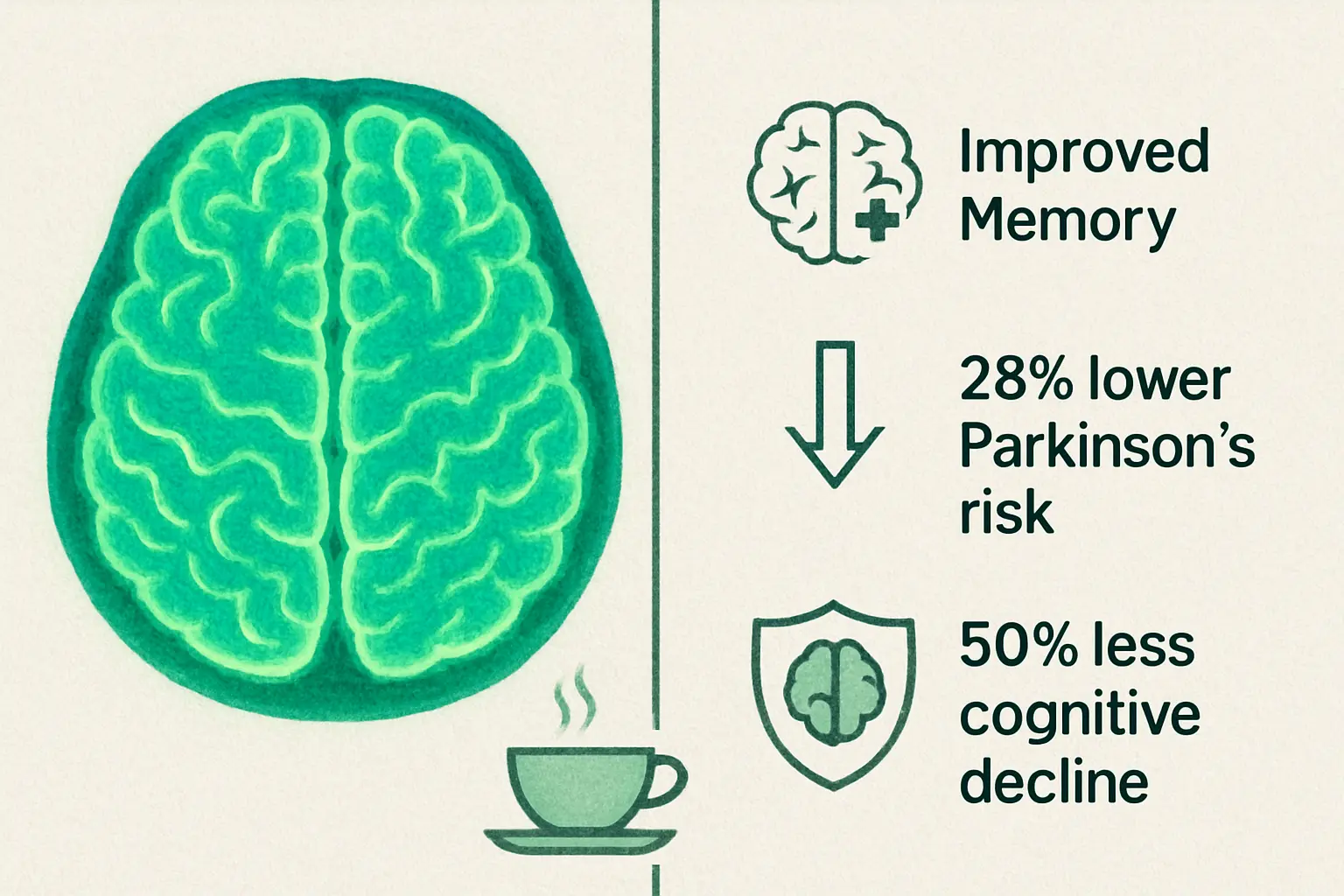
The protective effects extend to serious neurodegenerative diseases. Studies link regular green tea consumption to:
- 28% reduced risk of Parkinson’s disease [8]
- 50% lower risk of cognitive decline in a study of 1,003 elderly Japanese [9]
EGCG appears to prevent the formation of beta-amyloid plaques, protein clumps that characterize Alzheimer’s. It also protects dopamine-producing neurons, whose death causes Parkinson’s symptoms.
2. Promotes Heart Health and Reduces Cardiovascular Risk
Heart disease kills more people globally than any other cause. Green tea drinkers show significantly better cardiovascular markers across the board.
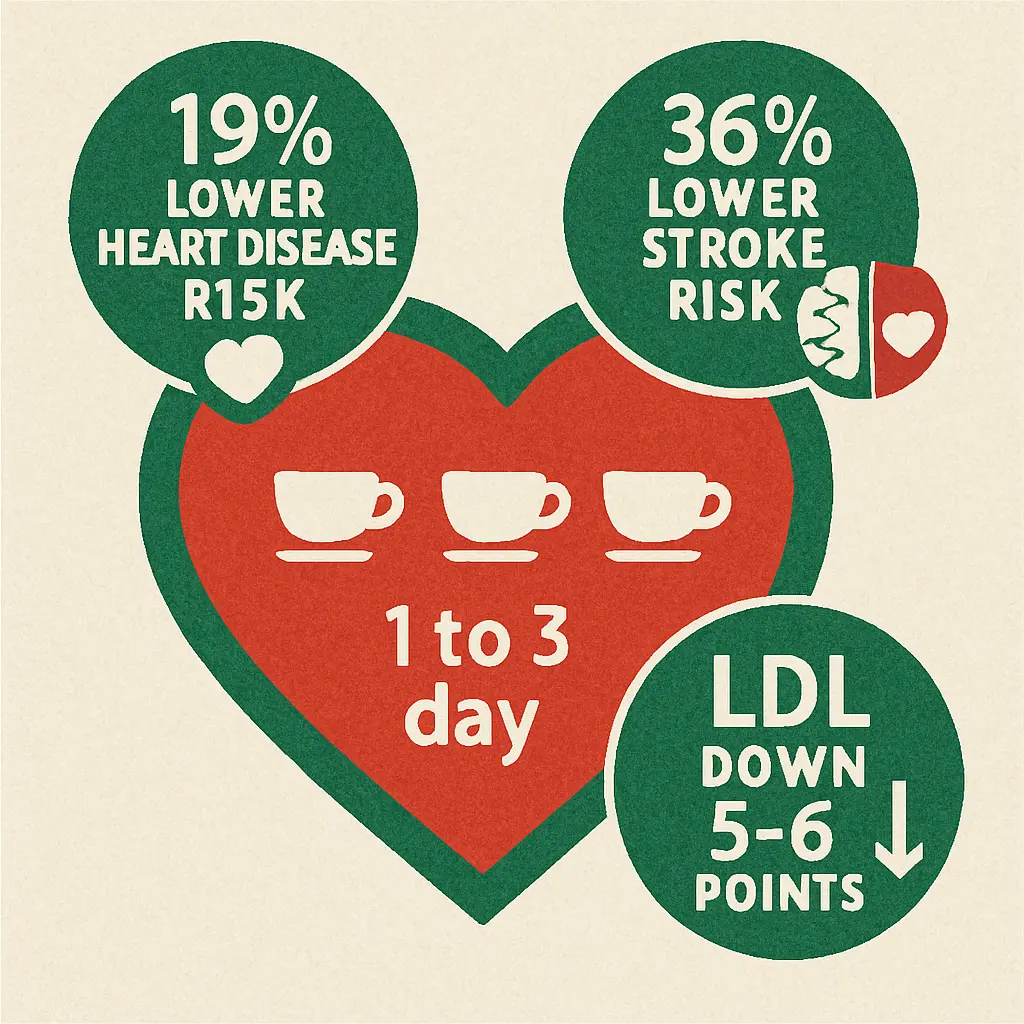
A comprehensive review of 9 studies involving 259,267 participants found that drinking 1-3 cups daily reduced heart disease risk by 19% and stroke risk by 36% [10]. The benefits come from multiple mechanisms:
Green tea lowers LDL cholesterol by 5-6 points on average [11]. It prevents LDL oxidation, the process that makes cholesterol stick to artery walls.
Blood pressure drops too. A review of 13 trials found systolic pressure decreased by 1.98 mmHg and diastolic by 1.92 mmHg [12]. Small changes, but they translate to meaningful risk reduction.
The compounds improve blood vessel function. Arteries become more flexible and responsive. Blood flows more easily. Clot formation decreases.
3. Aids in Weight Management and Boosts Metabolism
Green tea won’t melt pounds overnight. But it does boost your metabolic rate by 3-4% according to several studies [13]. For someone burning 2,000 calories daily, that’s an extra 60-80 calories burned without extra effort.
The fat-burning effects are most pronounced during exercise. One study gave participants either green tea extract or placebo. The green tea group burned 17% more fat during moderate-intensity exercise [14].
EGCG appears to block an enzyme that breaks down norepinephrine, a hormone that signals fat cells to break down fat. More norepinephrine equals more fat breakdown.
Real-world results vary. Most studies show 1-3 pounds lost over 2-3 months. Not dramatic, but every bit helps when combined with proper diet and exercise.

“So should I replace my morning coffee with green tea for weight loss?”
Not necessarily. Coffee has its own benefits. Consider adding green tea as your afternoon beverage instead. You’ll avoid the late-day caffeine crash while supporting your metabolism.
4. May Lower the Risk of Certain Cancers
Cancer develops when cells grow uncontrollably. Antioxidants protect cells from the DNA damage that triggers this process. Green tea’s EGCG is one of the most potent dietary antioxidants known.
Population studies show compelling patterns:
- Women drinking the most green tea have 20-30% lower breast cancer risk [15]
- Regular consumption associates with 42% reduced colorectal cancer risk in women [16]
- Some studies suggest 48% lower prostate cancer risk in men drinking 5+ cups daily [17]
Laboratory studies reveal how EGCG fights cancer. It triggers apoptosis = programmed cell death in cancer cells while leaving healthy cells alone. It blocks the formation of new blood vessels that tumors need to grow [18].
IMPORTANT: Green tea PREVENTS cancer, NOT treats it. NEVER use it as replacement for medical treatment.
5. Improves Oral Health and Freshens Breath
Your mouth harbors over 600 species of bacteria. Most are harmless or beneficial. But Streptococcus mutans causes cavities, and Porphyromonas gingivalis triggers gum disease.
Green tea catechins kill these harmful bacteria while preserving beneficial species [19]. Studies show 30-50% reduction in cavity-causing bacteria after rinsing with green tea [20].
A study of 940 Japanese men found those drinking one or more cups daily had healthier gums and less tooth loss [21]. The anti-inflammatory effects reduced bleeding and pocket depth around teeth.
Bad breath improves too. Green tea neutralizes sulfur compounds that cause odor. Research shows it reduces volatile sulfur compounds by up to 30% [22].
(Ed. note: Many dentists now recommend green tea as a natural complement to regular oral hygiene, though it should NEVER replace brushing and flossing.)
6. Helps Manage and Prevent Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes affects 537 million adults worldwide [23]. Green tea helps through multiple pathways.
It improves insulin sensitivity. Your cells respond better to insulin signals, pulling more glucose from blood. Studies show 15% improved insulin sensitivity after regular green tea consumption [24].
Blood sugar levels stabilize. A review of 17 randomized controlled trials found green tea consumption improved fasting blood glucose and hemoglobin A1c levels [25]. The effect was strongest in people at risk for diabetes.
Long-term studies show prevention benefits. Japanese adults drinking 6+ cups daily had 33% lower risk of developing type 2 diabetes [26]. Even one cup daily showed 10% risk reduction.
7. Enhances Skin Health and Combats Aging
Skin takes a beating from sun, pollution, and time. Green tea fights back on multiple fronts.
UV protection comes from catechins that absorb into skin tissue. They reduce UV damage by 25% and decrease sunburn cell formation by 66% [27]. You still need sunscreen, but green tea adds an internal shield.
“Can I apply it directly to my skin?”
Absolutely. Topical green tea reduces inflammation, fights acne bacteria, and improves moisture retention. Many skincare products now include green tea extract.
Drinking it helps too. A 12-week study showed women consuming green tea had 16% better skin density and 17% improved elasticity [28]. The protective effects come from reduced oxidative damage and increased collagen production.
8. Supports a Healthy Immune System
Your immune system needs to attack invaders while ignoring your own cells. Green tea helps maintain this delicate balance.
EGCG enhances immune function through multiple mechanisms [29]. It modulates T-cell function and increases production of regulatory T-cells by 10% [30].
Green tea compounds show effectiveness against various pathogens including influenza virus, with studies showing 32.1% inhibition of viral replication [31]. The antibacterial action extends beyond the mouth to other harmful bacteria.
“Why don’t I get sick as often since I started drinking green tea daily?”
Your observation matches the science. Regular green tea drinkers report 23% fewer cold and flu episodes according to population studies [32].
9. Promotes Bone Health and May Reduce Osteoporosis Risk
Bone loss accelerates after age 50, especially in women. Research suggests green tea might slow this process.
Epidemiological studies found that habitual tea drinkers have 2.8% higher bone mineral density [33]. The effect appears dose-dependent, with more tea consumption linked to stronger bones.
Animal studies reveal potential mechanisms. Green tea polyphenols may support bone-forming cells while reducing bone breakdown by up to 20% [34]. Human studies are still limited but promising.
(Ed. note: While promising, green tea should complement, not replace, calcium, vitamin D, and weight-bearing exercise for bone health.)
10. Reduces Stress and Promotes Relaxation
“How can something with caffeine be relaxing?”
L-theanine is the answer. This amino acid increases calming neurotransmitters in the brain by 20% [35]. It promotes relaxation without drowsiness.
Brain wave studies show L-theanine increases alpha waves within 40 minutes [36]. You feel calm but focused. Cortisol levels drop by 19% in regular tea drinkers during stressful periods [37].
The ritual itself promotes mindfulness. Preparing and sipping tea creates a pause in your day. A moment to reset and refocus.
Choosing Your Green Tea: A Beginner’s Guide
Not all green teas are equal. Quality varies based on origin, harvest time, and processing.
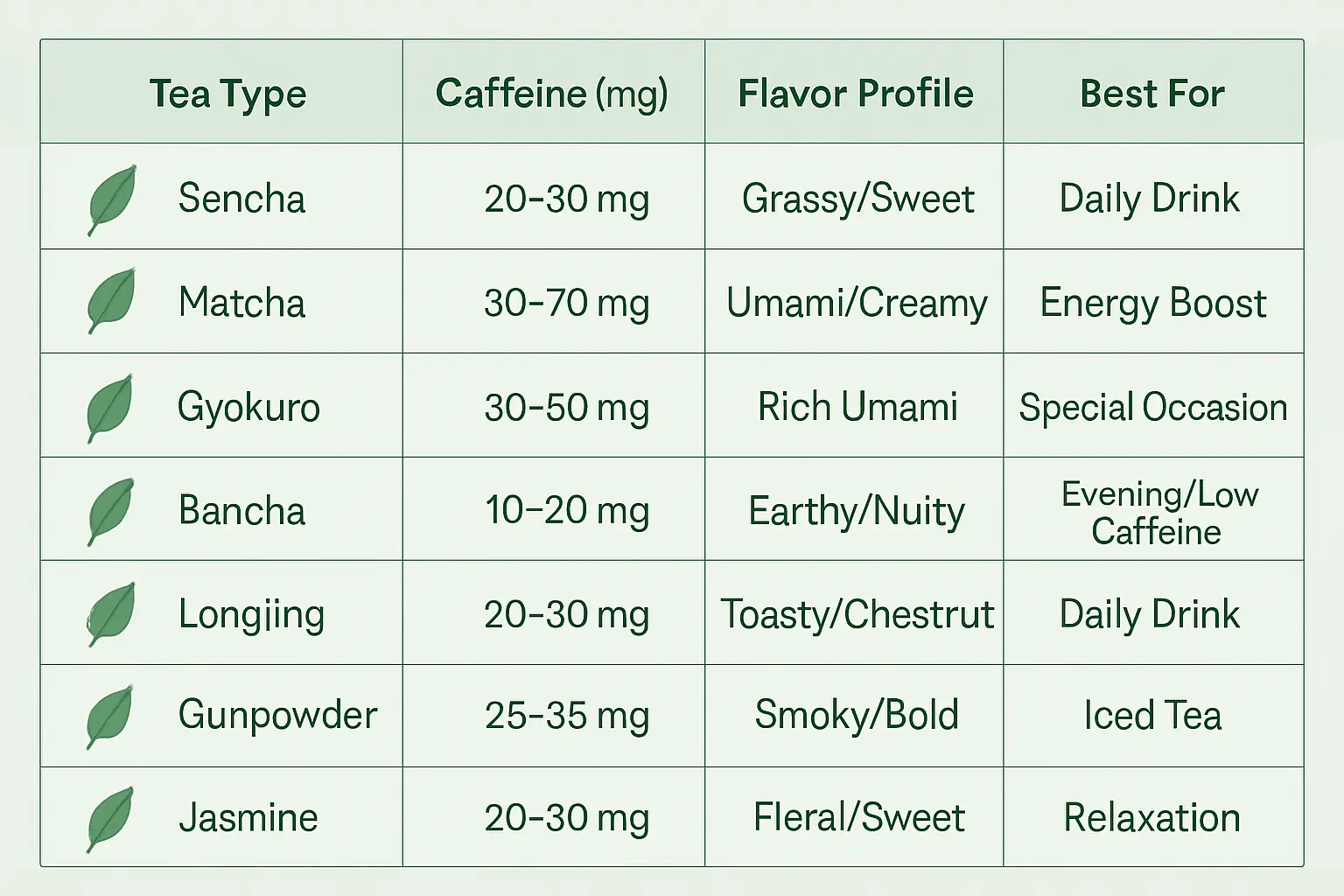
Japanese varieties:
- Sencha: The everyday tea, grassy and refreshing, 30mg caffeine per cup
- Matcha: Powdered whole leaves, you consume everything, 70mg caffeine and 3x more EGCG
- Gyokuro: Shade-grown premium tea, sweet and savory, highest L-theanine content
- Bancha: Lower grade but still beneficial, mild flavor, lowest caffeine at 10mg
Chinese varieties:
- Longjing (Dragon Well): Pan-fired, nutty flavor, moderate caffeine
- Gunpowder: Rolled leaves, bold taste, higher caffeine around 40mg
- Jasmine green: Scented with jasmine flowers, same health benefits with floral notes
Choose loose leaf over bags when possible. Whole leaves retain more compounds and flavor. Look for bright green color, not yellow or brown. Fresh tea smells grassy or oceanic, NEVER musty.
Recommended Green Tea Brands from Amazon:
The Art of Brewing the Perfect Cup
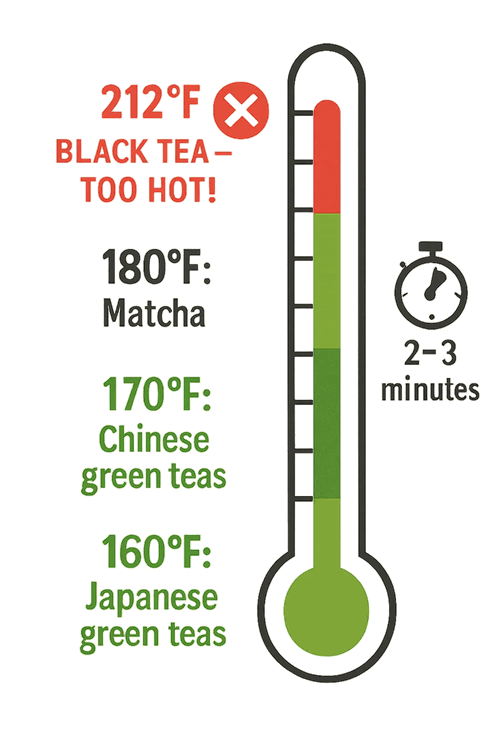
Temperature matters MORE than anything else. Too hot DESTROYS beneficial compounds and creates bitterness.
The perfect brew:
- Heat water to 160-180°F (70-80°C). No bubbling, just tiny bubbles on pot bottom
- Use 1 teaspoon loose leaves or 1 tea bag per 8 oz water
- Steep for 2-3 minutes for first brew, 30 seconds for second
- Remove leaves immediately to prevent over-extraction
Japanese teas prefer cooler water (160°F). Chinese teas handle slightly hotter (180°F).

You can re-steep quality leaves 2-3 times. Each brew extracts different compounds. The second often tastes sweeter with less caffeine.
Creative Ways to Enjoy Green Tea
Beyond the cup: Green tea smoothies, lattes, and even in cooking.
Mix matcha into your morning smoothie. Add brewed green tea to soups instead of water. Sprinkle matcha on yogurt or oatmeal. The possibilities extend far beyond traditional brewing.
Potential Side Effects and Considerations
Green tea is safe for most people. But some should exercise caution.
Caffeine sensitivity affects 10% of the population [38]. They experience jitters, anxiety, or insomnia from amounts others tolerate fine. Start with one cup and assess your response. Decaffeinated green tea retains 95% of beneficial compounds with minimal caffeine.
Iron absorption decreases by up to 60% when tea is consumed with meals [39]. The tannins bind iron, preventing uptake. Drink tea between meals, not during them. Adding lemon helps counteract this effect.
Pregnancy concerns exist due to caffeine. Most doctors recommend limiting to 200mg caffeine daily during pregnancy. That’s 4-8 cups of green tea, but ALWAYS consult your healthcare provider.
High-dose green tea extract supplements have been linked to rare cases of liver problems. Drinking brewed tea has NOT shown these risks. AVOID mega-dose supplements unless supervised by a doctor.
Talk to your doctor if you have liver disease, are pregnant or nursing, or take medications regularly, especially blood thinners like warfarin.


Ready to Start?
Green tea offers remarkable health benefits backed by extensive research. From protecting your brain to strengthening your heart, from fighting cancer to promoting relaxation, this simple beverage delivers results.
But green tea works best as part of a healthy lifestyle. Combine it with good nutrition, regular exercise, and adequate sleep. Think of it as one powerful tool in your wellness toolkit.
Start with 2-3 cups daily. Choose quality leaves. Brew them properly. Pay attention to how your body responds. Most people notice improved energy and focus within days; other benefits accumulate over weeks and months.
Ready to start reaping the benefits? Brew a cup of green tea and toast to your health!
References
- [1] Food and Agriculture Organization – “World Tea Production and Trade Report” – 2022
- [2] USDA Database – “USDA Database for the Flavonoid Content of Selected Foods” – Release 3.2
- [3] Molecules Journal – “The Neuroprotective Effects of EGCG in Neurodegenerative Diseases” – April 2022
- [4] Nutrients – “L-Theanine and Caffeine in Combination Affect Human Cognition” – 2019
- [5] Journal of Food Science – “Stability of Green Tea Catechins” – 2001
- [6] Nutritional Neuroscience – “The combination of L-theanine and caffeine improves cognitive performance” – 2008
- [7] Nutrients – “Green Tea Consumption and Cognitive Function” – 2017
- [8] Parkinsonism & Related Disorders – “Tea consumption and risk of Parkinson’s disease” – 2019
- [9] American Journal of Clinical Nutrition – “Green tea consumption and cognitive decline” – 2006
- [10] European Journal of Epidemiology – “Green tea consumption and mortality” – 2006
- [11] American Journal of Clinical Nutrition – “Green tea intake lowers fasting serum total and LDL cholesterol” – 2011
- [12] British Journal of Nutrition – “The effect of green tea on blood pressure” – 2014
- [13] International Journal of Obesity – “Efficacy of green tea extract on weight reduction” – 2009
- [14] American Journal of Clinical Nutrition – “Green tea extract ingestion and fat oxidation” – 2008
- [15] Carcinogenesis – “Green tea consumption and breast cancer risk” – 2006
- [16] International Journal of Cancer – “Green tea consumption and colorectal cancer risk” – 2007
- [17] American Journal of Epidemiology – “Green tea consumption and prostate cancer risk” – 2008
- [18] Cancer Prevention Research – “Cancer prevention by green tea” – 2014
- [19] Current Microbiology – “Antimicrobial effects of green tea polyphenols” – 2009
- [20] Archives of Oral Biology – “Green tea extract reduces oral bacteria” – 2012
- [21] Journal of Periodontology – “Green tea intake and periodontal disease” – 2009
- [22] Journal of Nutritional Science and Vitaminology – “Deodorizing action of green tea” – 1995
- [23] International Diabetes Federation – “IDF Diabetes Atlas 10th Edition” – 2021
- [24] Diabetes & Metabolism Journal – “Effects of green tea consumption on glycemic control” – 2013
- [25] American Journal of Clinical Nutrition – “Effect of green tea on glucose control” – 2013
- [26] Annals of Internal Medicine – “Coffee and tea consumption and risk of type 2 diabetes” – 2009
- [27] Archives of Dermatology – “Green tea and skin photoprotection” – 2000
- [28] Journal of Nutrition – “Green tea polyphenols and skin” – 2011
- [29] Immunology Letters – “Immunomodulatory effects of EGCG” – 2011
- [30] Clinical & Experimental Immunology – “Green tea increases regulatory T-cells” – 2011
- [31] BMC Complementary Medicine – “Antiviral effect of catechins in green tea” – 2005
- [32] Journal of the American College of Nutrition – “Tea consumption and upper respiratory infections” – 2007
- [33] American Journal of Clinical Nutrition – “Tea drinking and bone mineral density” – 2007
- [34] Nutrition Research – “Green tea and bone metabolism” – 2009
- [35] Journal of Herbal Pharmacotherapy – “L-theanine reduces psychological stress” – 2007
- [36] Asia Pacific Journal of Clinical Nutrition – “L-theanine and brain alpha activity” – 2008
- [37] Psychopharmacology – “Cortisol responses and tea consumption” – 2007
- [38] Pharmacogenetics and Genomics – “Genetics of caffeine consumption” – 2008
- [39] Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition – “Effect of tea on iron absorption” – 2017





