Potato Vs Sweet Potato: Nutrients, Glycemic Index, Weight Loss

Are you curious about which potato is healthier: potato vs sweet potato? The debate has been ongoing, but we’re here to provide you with evidence-based information to help you make an informed decision.
In this article, we’ll compare the nutritional content, glycemic index, antioxidant levels, and carbohydrate content of both potatoes. We’ll also explore their impact on weight loss.
So sit back and get ready to discover the truth about these tubers!
About Potatoes and Sweet Potatoes: Origins, Facts, Family
Potatoes and sweet potatoes are both root vegetables that belong to the same family but have different origins and nutritional profiles.
Potatoes, scientifically known as Solanum tuberosum, originated in South America and were brought to Europe by Spanish explorers in the 16th century. They come in various colors like white, yellow, and red, with a starchy texture when cooked.
On the other hand, sweet potatoes, scientifically known as Ipomoea batatas, are native to Central America and have been cultivated for thousands of years. They are usually orange or purple in color and have a sweeter taste compared to regular potatoes.
In terms of nutrition, both potatoes and sweet potatoes offer unique benefits. Potatoes are a good source of carbohydrates and provide essential nutrients like vitamin C, potassium, and dietary fiber. However, they tend to have a higher glycemic index which can lead to spikes in blood sugar levels.
Sweet potatoes are rich in beta-carotene which is converted into vitamin A in our bodies. They also contain vitamins C and B6 along with minerals like potassium and manganese. Additionally, sweet potatoes have a lower glycemic index compared to regular potatoes due to their higher fiber content.
Overall, both types of root vegetables can be part of a healthy diet when consumed in moderation. It ultimately depends on your personal preferences and nutritional needs when deciding between regular potatoes or sweet potatoes.
Potato vs sweet potato nutritional information
Comparing the nutritional information, it’s clear that sweet potatoes offer more vitamins and minerals than regular potatoes. While both types of potatoes are nutritious, sweet potatoes have a slight edge when it comes to their nutrient content.
Here is a comparison of the nutritional values of 100 grams of each type:
| Nutrient | Sweet Potato (per 100g) | Potato (per 100g) |
|---|---|---|
| Water | 77.3g | 79.2g |
| Energy | 86 kcal | 77 kcal |
| Protein | 1.57g | 2.05g |
| Total Fat | 0.05g | 0.09g |
| Carbohydrates | 20.1g | 17.5g |
| Dietary Fiber | 3g | 2.1g |
| Sugars | 4.18g | 0.82g |
| Starch | 12.6g | 15.3g |
| Calcium | 30mg | 12mg |
| Iron | 0.61mg | 0.81mg |
| Magnesium | 25mg | 23mg |
| Phosphorus | 47mg | 57mg |
| Potassium | 337mg | 425mg |
| Sodium | 55mg | 6mg |
| Vitamin C | 2.4mg | N/A |
| Vitamin B-6 | 0.209mg | 0.298mg |
| Folate | 11µg | 15µg |
| Vitamin A (RAE) | 709µg | 0µg |
| Vitamin K (phylloquinone) | 1.8µg | 2µg |
As you can see from the table, sweet potatoes contain slightly more calories and carbohydrates compared to regular potatoes. However, they also provide more fiber which aids in digestion and helps maintain a healthy weight.
What sets sweet potatoes apart is their high vitamin A content. They are an excellent source of this essential vitamin, providing over three times the amount found in regular potatoes. Vitamin A plays a crucial role in maintaining good vision, supporting immune function, and promoting healthy skin.
While regular potatoes still offer several important nutrients like potassium and vitamin C, sweet potatoes clearly have an advantage in terms of overall nutrient density. So if you’re looking to maximize your intake of vitamins and minerals, choosing sweet potatoes would be a healthier option.
Potato vs Sweet Potato Glycemic Index: How the Glycemic Index of both potato species compare?
If you’re trying to manage your blood sugar levels, it’s important to consider the glycemic index of both types of potatoes. The glycemic index (GI) is a scale that measures how quickly and how much a food raises your blood sugar levels after you eat it. A high GI indicates a rapid increase in blood sugar, while a low GI means a slower and more gradual rise.
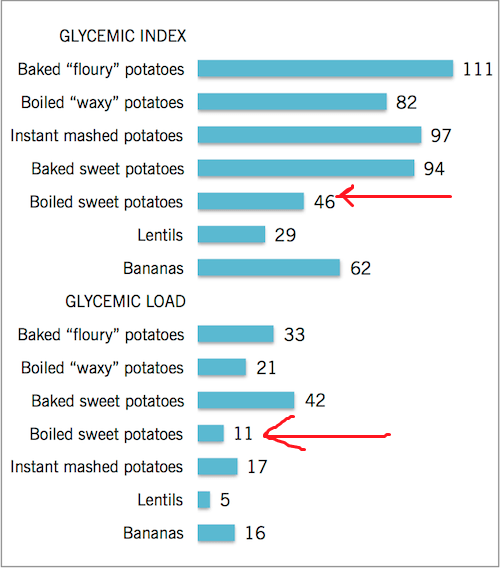
When comparing the glycemic index of regular potatoes and sweet potatoes, there are some differences to note.
Regular potatoes have a higher GI compared to sweet potatoes. This means that regular potatoes can cause a quicker spike in blood sugar levels after consumption. Sweet potatoes, on the other hand, have a lower GI and are considered to have more stable effects on blood sugar.
However, it’s important to remember that the preparation method can also impact the glycemic index of both types of potatoes. Cooking methods such as boiling or baking can lower the GI of regular potatoes, making them less likely to cause sharp spikes in blood sugar levels.
Potato vs Sweet Potato Antioxidant Content
Although regular potatoes and sweet potatoes have different glycemic indexes, their antioxidant content is something worth considering. Both types of potatoes contain phytochemicals that help regulate the immune system, fight viruses and pathogens, control inflammation, and inhibit tumor growth.
These phytochemicals include carotenoids, ascorbic acid, tocopherols, polyphenols, alpha-lipoic acid, selenium, lycopene, chlorogenic acid, and many others.
Colored varieties of potatoes and sweet potatoes tend to have higher levels of these beneficial plant chemicals. For example, red-fleshed or purple-fleshed potatoes are comparable to Brussels sprouts, blueberries or spinach in terms of their antioxidant content. This means that incorporating these colorful varieties into your diet can provide you with a range of health benefits.
Antioxidants play a crucial role in protecting our cells from oxidative damage caused by free radicals. By neutralizing these harmful molecules, antioxidants help prevent chronic diseases such as heart disease and cancer.
Potato vs Sweet Potato Carbs: How much carbohydrates 100 gram have?
Regular potatoes are a good source of carbohydrates, providing around 17 grams per 100 grams serving. These carbohydrates come mainly in the form of starch, which is broken down into glucose during digestion to provide energy for your body.
On the other hand, sweet potatoes contain slightly more carbohydrates than regular potatoes, with approximately 20 grams per 100 gram serving. The majority of these carbohydrates in sweet potatoes also come from starch but they also contain some natural sugars.
Despite having a higher carbohydrate content compared to regular potatoes, sweet potatoes have a lower glycemic index due to their higher fiber content and slower digestion rate. This means that they cause a slower and more gradual rise in blood sugar levels after consumption compared to regular potatoes.
Starch in sweet potatoes vs potatoes
Starch is a type of carbohydrate that provides energy to your body. Both sweet potatoes and regular potatoes contain starch, but the amount may vary.
Between white potatoes and sweet potatoes, white potatoes generally contain more starch. White potatoes, particularly the high-starch varieties like Russet potatoes, have a higher starch content compared to sweet potatoes. This higher starch content in white potatoes contributes to their fluffy and mealy texture when cooked, making them great for mashing and frying.
Sweet potatoes, on the other hand, have less starch and more sugars, which gives them their characteristic sweet flavor. The starch in sweet potatoes is of a different type than that found in white potatoes, and it’s often broken down into sugars during cooking, contributing to their sweetness.
Here’s a simple breakdown comparing the carbohydrate and starch content in regular white potatoes and sweet potatoes:
| Nutrient Content (per 100g) | White Potatoes | Sweet Potatoes |
|---|---|---|
| Carbohydrates | 17.49g | 20.71g |
| – Starch | 15.72g | 6.70g |
| – Sugars | 0.82g | 4.18g |
Please note that these values are approximate and can vary based on factors such as the specific variety of potato and its growing conditions.
Which is Better for Weight loss? Potatoes or Sweet Potatoes? How much calories each potato type have
If you’re looking to lose weight, it’s important to consider the calorie content of both types of potatoes. Potatoes and sweet potatoes differ in their calorie content, which can impact weight loss efforts.
A medium-sized baked potato with skin has approximately 161 calories, while a medium-sized baked sweet potato with skin contains about 103 calories. Therefore, if you’re trying to limit your calorie intake for weight loss purposes, opting for sweet potatoes might be a better choice.
However, it’s crucial to note that the calorie difference between the two types of potatoes is not significant. Both are relatively low in calories compared to other foods. Additionally, the primary factor influencing weight loss is overall calorie intake and expenditure throughout the day, rather than focusing solely on one food item.
Frequently Asked Questions
Conclusion: Which potato is healthiest?
In summary, both types of potatoes can be part of a healthy diet. While there are some differences between regular potatoes and sweet potatoes, they both offer various health benefits and can be enjoyed in moderation.
Regular potatoes, such as russet or red potatoes, are a good source of vitamins C and B6, potassium, and dietary fiber. On the other hand, sweet potatoes are rich in vitamin A (in the form of beta-carotene), vitamin C, manganese, and dietary fiber.
When it comes to weight loss, choosing either type of potato can work as long as they are prepared in a healthy manner. Both regular and sweet potatoes have similar calorie content when cooked without added fats or toppings. For example, one medium-sized baked potato has around 160-170 calories while one medium-sized baked sweet potato has around 100-120 calories.
Ultimately, the healthiest choice depends on your personal preferences and nutritional needs. Regular potatoes may be preferred if you need more potassium or vitamin B6 in your diet. On the other hand, if you’re looking for more vitamin A or fiber intake, sweet potatoes would be a great option.
Remember that portion control is key when incorporating any type of potato into your diet. Balancing your meals with a variety of nutrient-dense foods will ensure overall health and well-being.
More Food Comparison Articles
