Zinc (Zn) Benefits, Deficiency, Side Effects, Absorption, RDA

Zinc (ZN) belongs to the micronutrients, as it is an essential mineral, which the human body needs in very small quantities. It has the second highest concentration in the human body after iron, and plays an important role in many of the body’s basic functions.
What is Zinc
Zinc is an essential component for more than 100 enzymes involved in the digestion and utilization of fat, protein and carbohydrates by the body, and is closely linked to the energy production process.
It is essential for the proper functioning of the immune system and protection of the body from infections and viruses, and helps in the wound healing process.
Its role in DNA synthesis and in the reproduction and development of the body’s cells makes it a vital element for normal development during pregnancy, childhood and adolescence. Finally, zinc is essential for the sense of taste and smell.
Zinc is present everywhere in the human body. It is the most abundant metal in the intracellular space.
It is absorbed from food through the small intestine and then transported into the blood with the help of albumin and alpha-macroglobulin, but only 0.1% of the total zinc content in the body is found in the blood.
95% of the zinc is in the cells. An adult male has about 2 grams of zinc in his body, of which 57% is found in skeletal muscle, 30% in bone and 4-6% in skin.
Zinc Benefits
Zinc has three different types of function in the human body: catalytic, structural and regulatory. Here are some of the most important zinc health benefits.
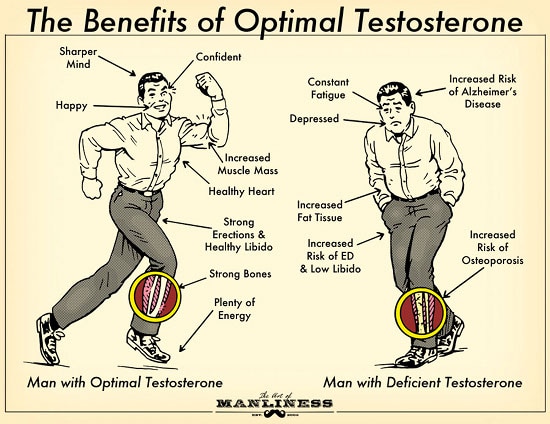
Zinc Deficiency
Zinc is necessary to be taken daily through the diet, as the body has no specialized system for its storage. Zinc deficiency is manifested by the following symptoms:
Vegetarians may be at increased risk for zinc deficiency, people on crash diets, anorexics, people who use soy as a meat substitute, pregnant and breastfeeding women, people with gastrointestinal disorders, alcoholics and the elderly.
The Global Zinc Shortage
Research conducted over the past few years shows that zinc deficiency is affecting the health and well-being of populations around the world. The International Zinc Advisory Group (IZiNCG) has estimated that the prevalence of zinc deficiency is 31% worldwide, ranging from 4% to 73%, with the highest rates of deficiency and the most severe effects of zinc deficiency occurring mainly in African, Eastern Mediterranean and South-East Asian countries.
It has been estimated that 1/3 of the world’s population resides in countries at high risk of deficiency, with infants, young children, pregnant and lactating mothers being the most vulnerable groups due to their increased zinc needs.
Zinc supplementation programs, which have been implemented in developing countries, have been shown to result in reduced incidence and severity of diarrhea, pneumonia and possibly malaria, and lower mortality rates in children.
In addition, zinc supplements have helped improve growth and weight gain in malnourished and underweight children, and there is evidence that zinc supplementation in pregnant women can prevent adverse pregnancy outcomes, contribute to postpartum weight gain and reduce infections.
Read Also: Manganese Health Benefits, Sources, Deficiency, RDA
Zinc Food Sources
Zinc is found in a wide range of foods. The richest sources are high-protein foods.
The phytic acids found in foods of plant origin bind zinc and prevent its absorption. Thus, people who exclude meat from their diet should include dairy products, eggs, whole grains, nuts and pulses in order to obtain adequate amounts of zinc.
Best Zinc Food Sources
| Foods | Description | Zinc (mg/100 g) |
|---|---|---|
| Oysters | Raw | 55 – 136 |
| Pumpkin seeds | 10,3 | |
| Sesame seeds | 10,2 | |
| Liver | Raw, Calf | 7,8 |
| Black Chocolate | 6,8 | |
| Legumes | Raw | 5,5 |
| Beef | Without fat | 4,3 |
| Lamp | Without fat | 4,0 |
| Pork | Without fat | 2,4 |
| Wheat flour | Whole meal | 2,9 |
| Mussels | Boiled | 2,2 |
| Octapus | Boiled | 2,2 |
| Sunflower seeds | 2 | |
| Rice | Raw, White. | 1,8 |
| Crabs | Boiled | 1,3 – 5 |
| Chicken | Raw | 1,1 |
| Eggs | Chicken, whole, raw | 0,5 – 3,3 |
| Cheese | 0,2 – 5,0 | |
| Yoghurt | From full fat milk | 0,5 – 0,7 |
| Cod | Rw | 0,3 – 0,5 |
| Green leafy vegetables | 0,2 – 0,6 | |
| Cow’s milk | 0,4 | |
| Fruits | (On average) | 0,4 |
| Potatoes | Raw | 0,2 – 0,3 |
Zinc Toxicity
Severe acute toxicosis from excessive zinc intake has been described after ingestion of water stored in galvanised containers or after the use of such water during dialysis.
Side effects include nausea, vomiting and fever and occur after an acute intake of 2 grams or more of zinc.
Prolonged intakes of zinc in amounts well above normal (e.g. 75-300 mg per day) have been associated with a reduction in copper utilisation (causing microcytic anaemia and neutropenia), a reduction in immune responses and a drop in high-density lipoprotein levels.
However, some scientists argue that even a short-term intake of about 25-50 mg of zinc per day from dietary supplements can interfere with the metabolism of both iron and copper.

Recommended Daily Intake
The American Food and Nutrition Council has reported that there is no evidence of side effects from the intake of zinc contained in food.
However, it has settled on a maximum limit of 40 mg per day for adults over 19 years of age. This amount represents the total intake of zinc from food, water and dietary supplements including fortified foods.
The European Union has set a maximum limit of 25 mg per day.
The (American) recommendations for daily zinc intake are:
Zinc is lost through sweat and therefore athletes should obtain adequate amounts from their diet. Note that some studies have found low testosterone in athletes and it may be that the cause is the loss of zinc. Diabetics also lose zinc through urine.
Recommended Zinc Supplements
While there are hundreds of different zinc supplements on the market we recommend the following zinc supplements for their proven consistency in delivering quality zinc products.
1️⃣ Microingredients Zinc Picolinate with Vitamin C, 365 Capsules
2️⃣ Microingredients, Zinc Complex, 200 Capsules
3️⃣ Pure Encapsulations Zinc 30 – 60 Capsules
4️⃣ Garden of Life Vitamin Code® – Raw Zinc – 60 Vegan Capsules
5️⃣ Integrative Therapeutics Zinc-Carnosine – 60 Vegetable Capsules
Final Take
Zinc is an essential mineral involved in the regulation of many enzymes in the human body. It also has antioxidant activity and is used in dietary supplements that help the immune system.
It is present in dozens of proteins called metalloproteins including the enzyme superoxide dismutase, an endogenous antioxidant that includes both zinc and copper. It is also needed for the conversion of cholesterol to testosterone.
