What is BDNF Protein And What Does It Do?

Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) is a protein that plays a vital role in the development, growth, and maintenance of neurons in the brain.
It is involved in a variety of functions, including learning and memory, as well as the regulation of mood and behavior. Deficiencies in BDNF have been linked to a number of neurological and psychiatric disorders, including depression, anxiety, and Alzheimer’s disease.
In this article, we will explore the role of BDNF in the brain and its potential as a therapeutic target for the treatment of various disorders.
What is BDNF Protein?
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) is a protein that belongs to the neurotrophin family of growth factors.
It is produced and secreted by neurons, and it plays a crucial role in the development, survival, and function of nerve cells in the brain and nervous system.
BDNF acts on specific receptors called TrkB receptors, which are found on the surface of neurons.
When BDNF binds to these receptors, it activates signaling pathways that promote the growth, differentiation, and survival of neurons.
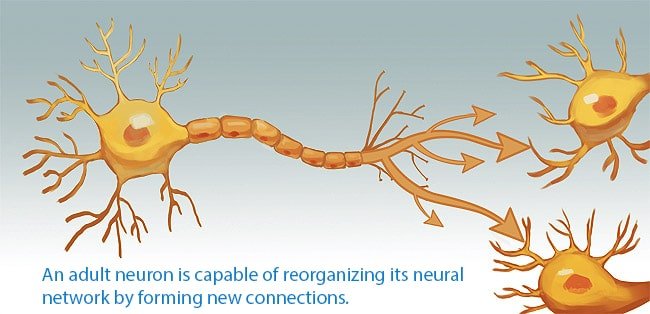
BDNF has a wide range of functions in the brain and nervous system. It is involved in the development and plasticity of the nervous system, including the formation of new connections between neurons (synapses) during learning and memory.
BDNF also plays a role in the regulation of mood and behavior, and it has been linked to the development of anxiety and depression.
In addition, BDNF is involved in the repair and regeneration of damaged neurons in the brain, and it has been shown to have neuroprotective effects in animal models of stroke and neurodegenerative diseases.
Why is it important?
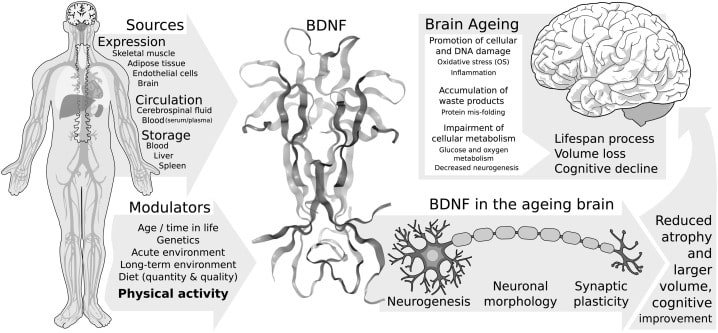
BDNF is important for a number of reasons. It plays a vital role in the development, growth, and maintenance of neurons in the brain and nervous system, and it is involved in a variety of functions, including learning and memory, as well as the regulation of mood and behavior.
Deficiencies in BDNF have been linked to a number of neurological and psychiatric disorders, including depression, anxiety, and Alzheimer’s disease. As such, BDNF has emerged as a potential therapeutic target for the treatment of these disorders.
BDNF is also involved in the repair and regeneration of damaged neurons in the brain, and it has been shown to have neuroprotective effects in animal models of stroke and neurodegenerative diseases.
This makes BDNF an important target for the development of treatments for conditions such as stroke and neurodegenerative diseases, which can cause significant damage to neurons in the brain and nervous system.
In addition, BDNF is involved in the development and plasticity of the nervous system, including the formation of new connections between neurons (synapses) during learning and memory.
Overall, BDNF is an important protein with a wide range of functions in the brain and nervous system, and it has significant potential as a therapeutic target for the treatment of a variety of neurological and psychiatric disorders.
How Can You Increase BDNF Protein Levels?
There are several ways that you can potentially increase BDNF protein levels in the brain:
- Exercise: Regular physical activity has been shown to increase BDNF levels in the brain. In particular, aerobic exercise, such as running or cycling, has been shown to be effective at increasing BDNF levels.
- Diet: A healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and omega-3 fatty acids has been associated with higher BDNF levels in the brain.
- Sleep: Getting enough sleep is important for maintaining overall health, and it has also been shown to increase BDNF levels in the brain.
- Stress management: Chronic stress has been linked to lower BDNF levels, so managing stress through techniques such as meditation, yoga, or other stress-reducing activities may help to increase BDNF levels.
- Environmental enrichment: Engaging in activities that challenge the brain, such as learning a new skill or hobby, has been shown to increase BDNF levels.
Foods that can help increase BDNF protein levels
There is limited research on specific foods that can increase BDNF protein levels, but a healthy diet that includes a variety of nutrients has been associated with higher BDNF levels in the brain. Some foods that may potentially help increase BDNF levels include:
- Omega-3 fatty acids: These healthy fats, found in foods such as fatty fish, nuts, and seeds, have been shown to increase BDNF levels and improve cognitive function.
- Blueberries: These colorful berries are rich in antioxidants and have been shown to increase BDNF levels in animal studies.
- Turmeric: This spice contains a compound called curcumin, which has been shown to increase BDNF levels and improve cognitive function in animal studies.
- Green tea: This beverage contains a class of antioxidants called catechins, which have been shown to increase BDNF levels in the brain.
- Dark chocolate: This treat is rich in antioxidants and has been shown to increase BDNF levels in animal studies.
Bottom Line
Overall, BDNF is a crucial protein that plays a vital role in the development and function of the nervous system. Its role in the regulation of neural plasticity and its potential involvement in the development of certain neurological and psychiatric disorders make it an area of active research and interest.
