The Impact of Semaglutide on Bariatric Surgery
In this article, we’re diving into the world of semaglutide and its impact, especially when it comes to weight loss and bariatric surgery.
If you’ve been wondering what semaglutide is all about, how it’s become a bit of a sensation in the weight loss scene, and why it’s making waves post-bariatric surgery, you’re in the right place.
We’ll break down its origins, its rise to fame, how it works, its benefits, and even touch on some possible side effects. Stick around, and by the end, you’ll have a solid grasp of why semaglutide is creating buzz in the health and wellness arena.
Let’s get into it!
What is Semaglutide?
If you’ve been paying attention to pop culture or have watched the news over the last year, you’ve probably heard about semaglutide and its use for weight loss.
Semaglutide, also known as Ozempic, Rybelsus, and most recently, Wegovy, is a prescription medication your doctor can prescribe.
The original use for semaglutide was to help reduce blood sugar in those who have type 2 diabetes and to reduce associated cardiovascular events, such as heart attack and stroke. [1]
Semaglutide was only available as a once-weekly injection, given subcutaneously (underneath the skin). During the last few years, increasing interest in the benefits of semaglutide has allowed the medication to become more widely available in different dosage forms and available brand names.
During post-market surveillance of Ozempic, a phase in which data continues to be reported to both the drug manufacturer and the FDA, healthcare providers reported significant weight loss among patients using semaglutide. [2]
Celebrities and influencers started promoting semaglutide as a “miracle drug” despite the fact that its original purpose was not for weight loss.

The medication experienced a remarkable surge in popularity and demand, leading to a staggering 152% increase in Ozempic prescriptions in 2023. A significant portion of these prescriptions were issued off-label for weight loss purposes.
What Does Off-Label Mean?
Doctors routinely prescribe “off-label” medications, indicating that they recommend the medication for a purpose different from its approved use by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA).
A medication’s intended use is also called its “indication.” When you learn that semaglutide is not “indicated” for weight loss, it signifies that the FDA has not granted approval for its use specifically for weight loss.
Medications not officially approved for a specific purpose typically don’t have as much research from the pharmaceutical company to show they work.
However, It doesn’t mean they don’t work; it just means the company hasn’t given the FDA enough paperwork to officially prove they work for that specific use.
This can complicate things when patients try to obtain the medication.
When a prescription is written for something besides what the FDA has approved it for, insurance companies will likely not cover the cost.
This has led the pharmaceutical industry to obtain more indications from the FDA for semaglutide. More recently, semaglutide in an oral tablet form, Rybelsus, has been approved. Wegovy, a higher dose, once-weekly injection, is specifically indicated for weight loss.
Why Has Semaglutide Become So Popular?
Movie stars, musicians, influencers, you name it. People have been talking about the life-changing results they have seen from medications like semaglutide.
There’s little doubt that semaglutide works for those struggling to lose weight, and research has shown that in conjunction with exercise, semaglutide can deliver amazing results.
In a recent study, participants receiving subcutaneous injections of semaglutide at doses of 1.7mg or 2.4mg experienced notable weight loss. [3]
At the three-month mark, the average weight loss was 6%, and by six months, it increased to an impressive 11%. Additionally, research indicates that the positive trend in weight reduction continues as long as patients maintain their weekly injection regimen.
The efficacy of this weekly injection has made it a valuable tool for individuals struggling with appetite control. Semaglutide and medications like it are emerging as a supportive option for patients in their weight loss journey.
The compelling results observed in these studies highlight the potential of semaglutide as a promising option for those seeking effective strategies to manage weight.
How Does Semaglutide Work?
Since semaglutide wasn’t initially approved for weight loss, you might be curious how it actually works.
The mechanism through which a medication operates is known as its “mechanism of action,” and semaglutide operates in multiple ways:
- Increases insulin: Semaglutide prompts your pancreas to release more insulin after a meal. Insulin is crucial for transporting glucose into your cells, where it can be used for energy.
- Decreases glucagon: By reducing the production of glucagon, semaglutide prevents your liver from releasing glucose into your bloodstream, helping to maintain lower blood sugar levels.
- Delays gastric emptying: Semaglutide slows down the emptying of your stomach contents, which can leave you feeling fuller for longer, resulting in the consumption of fewer calories.
Semaglutide is called a glucagon-like peptide receptor 1 agonist or GLP-1 agonist. [4]
Glucagon-like peptide is a naturally occurring hormone produced in the intestines. This hormone, often referred to as the “ileal brake,” is part of the body’s normal mechanisms for controlling appetite and slowing down digestion.
These mechanisms have proven effective in reducing blood sugar levels, making semaglutide a valuable tool for individuals with type 2 diabetes. Notably, doctors and patients have observed additional benefits of semaglutide beyond its primary role in lowering blood sugar.

How Does Semaglutide Help People Lose Weight?
Beyond its role in lowering blood sugar, semaglutide has proven beneficial for individuals dealing with weight-related issues. Here are key reasons why semaglutide is particularly effective for weight loss:
- Appetite Regulation: Semaglutide sends signals to the brain, indicating a sense of fullness. This, in turn, reduces the amount of food a person consumes.
- Controls Blood Sugar: Improved control of blood sugar levels helps diminish cravings for high-calorie foods, contributing to better overall dietary choices.
- Increased Basal Metabolic Rate: Semaglutide elevates the basal metabolic rate, which is the number of calories we burn while at rest. This means that even during periods of rest, individuals burn more calories, aiding in weight loss.
People may respond differently to the medication, so it’s crucial to listen to your healthcare provider and take semaglutide just as they tell you to.
To get the most out of the medication, try to include healthy habits in your daily routine, like exercising regularly and maintaining a balanced lifestyle. These habits can help boost your efforts to lose weight.

The Benefits of Semaglutide and Bariatric Surgery
While ongoing research is still exploring the advantages of semaglutide following bariatric surgery, recent studies have shown positive outcomes.
Bariatric surgery stands out as one of the most effective treatments for obesity, offering significant weight loss that can also lead to improvements in other weight-related health conditions. [5]
Conditions such as diabetes, high blood pressure, and the risk of stroke and heart attack can often see positive changes after successful bariatric surgery.
However, the success of bariatric surgery varies depending on several factors, and unfortunately, not everyone who undergoes the procedure can maintain their weight loss.
When someone regains weight after bariatric surgery, it’s referred to as “post-MBS weight recurrence” or “post-metabolic and bariatric surgery weight recurrence.”
Individuals experiencing post-MBS recurrence find themselves with limited treatment options. Frequently, revising the initial bariatric procedure becomes necessary for a patient to regain weight loss, a process that carries inherent risks.
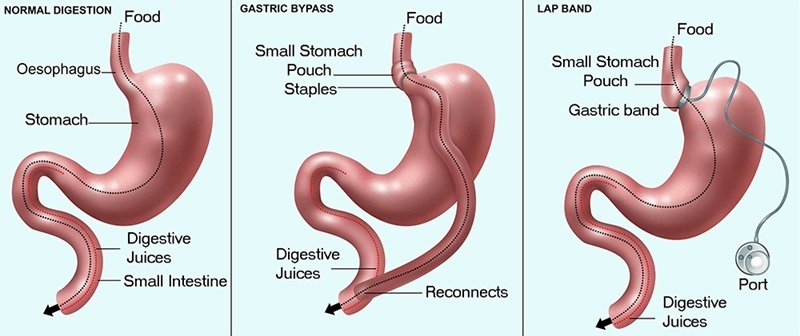
Health professionals have been exploring alternatives to additional surgery when a patient regains weight after the initial procedure. Recent research suggests that surgery may not be necessary after all.
In a recent study, researchers administered two GLP-1 agonists, semaglutide and Liraglutide, to patients dealing with post-MBS recurrence.
A total of 207 patients experiencing post-MBS recurrence were assigned either semaglutide or liraglutide and were closely monitored by researchers for a year. The outcomes of the study showed highly promising results.
The group taking semaglutide experienced an average weight loss of 13% in the first year of their treatment, while the Liraglutide group showed an average weight loss of 9%.
Although both groups exhibited significant weight reduction, semaglutide led to greater weight loss. Notably, 40% of patients using weekly semaglutide achieved a remarkable weight loss exceeding 15%
Semaglutide proves to be a valuable tool post-bariatric surgery, aiding in effective weight management. The GLP-1 receptor agonists play a role in appetite regulation, blood sugar control, and the increase of your basal metabolic rate. This combination holds promise as a solution to challenges related to obesity following surgery. As with any medication, it should be taken under the close supervision of a healthcare professional.
Possible Side Effects of Semaglutide
Every medication comes with potential side effects, which are documented through clinical trials and ongoing monitoring after the drug hits the market. Semaglutide, like all GLP-1 receptor agonists, carries some common side effects, including:
- Nausea: Feeling queasy, especially when first starting semaglutide, is a frequently reported side effect.
- Vomiting: Some individuals may experience vomiting within the initial treatments.
- Diarrhea: The delayed gastric emptying effect of semaglutide may cause diarrhea.
- Constipation: This is also a potential side effect related to delayed gastric emptying.
- Injection Site Reaction: An adverse reaction can occur at the injection site. Typically red, swollen, and itchy, it will resolve over time.
- Hypoglycemia: If semaglutide is added to other diabetes medications, there may be an increased risk of hypoglycemia.
It’s crucial to note that this list includes only some of the most commonly reported side effects. If you’re contemplating incorporating semaglutide to address obesity, discuss potential side effects with a healthcare professional to make an informed decision.
The Long-Term Effects of Semaglutide After Bariatric Surgery
This powerful pairing of effective weight loss solutions can be very promising. When there are multiple modalities of treatment options for patients, they can be used together to provide long-term results.
Bariatric surgery, when coupled with lifestyle adjustments, is a path forward to a healthier you. Similarly, semaglutide and other GLP-1 receptor agonists are demonstrating their efficacy in weight loss, yet they should not be perceived as instant fixes. With their broader application, the medical community now has the chance to integrate two powerful tools, enhancing outcomes for individuals contending with weight issues.
The combination of bariatric surgery and pharmacotherapy with semaglutide may help people reach their weight loss goals and keep excess weight off for good. The benefits and the risks should always be considered in consultation with a healthcare provider for both bariatric surgery and medications like semaglutide.
If you’re considering adding semaglutide after bariatric surgery, talk to your doctor about which treatment option is best for you.
Read Next
