Stemona Japonica Benefits (Bai Bu), Overview, History, Applications
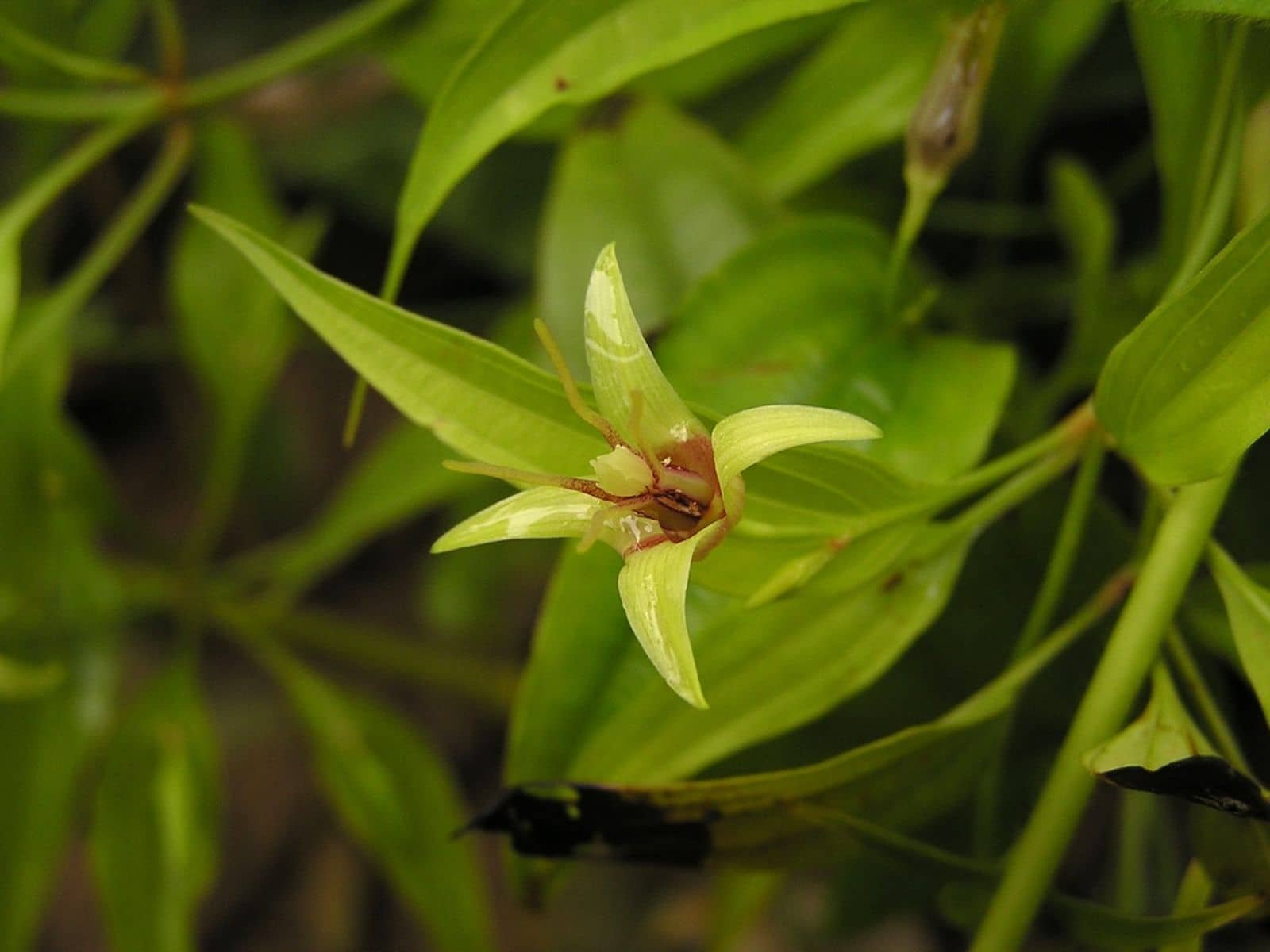

Stemona japonica, a herb widely used in traditional Chinese medicine, offers a range of health benefits particularly centred around respiratory ailments.
Known for its potent antitussive properties, it acts as an effective cough suppressant.
If you’re troubled by persistent coughs or other lung-related issues, extracts from this plant might provide relief. Its utilization stems from the belief that it can soothe the lung channel, leading to better breathing and relief from respiratory conditions.
Additionally, Stemona japonica is recognized for its anthelmintic and antiparasitic effects, making it a potentially useful remedy for parasitic infections.
The herb is thought to be beneficial against body lice, head lice, and several fungal infections like candidiasis.
People also use it to alleviate symptoms of itching and inflammation, common discomforts associated with these conditions.
Beyond its respiratory and antiparasitic applications, the herb is also cited for its role in managing phlegm and lung diseases, and even complex conditions such as tuberculosis.
Various Asian cultures have traditionally utilized the roots and rhizomes of a plant abundant in phytochemicals for its reputed health benefits.
Quick Overview
Here’s a table summarizing important facts about Stemona japonica:
| Attribute | Information |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Stemona japonica |
| Family | Stemonaceae |
| Common Names | Japanese stemona Stemona root |
| Native Region | East Asia (Japan, China, Korea) |
| Plant Type | Perennial herbaceous plant |
| Traditional Uses | – Used in traditional Asian medicine – Known for its antitussive (cough-suppressant) properties |
| Active Compounds | Alkaloids, including stenine and neostenine |
| Chemical Composition | Contains alkaloids with potential medicinal properties |
| Cultivation | Grows in well-drained, loamy soil in partial shade |
| Harvesting Time | Roots are typically harvested in the autumn |
| Conservation Status | Not globally assessed, varies by region |
| Medical Research | – Investigated for potential antitussive, antifungal, and antiparasitic properties |
| Potential Side Effects | Limited information available. |
| Caution | Some alkaloids may be toxic. |
Historical and Traditional Uses
Stemona japonica holds a prominent place within the world of holistic medicine practices. Its therapeutic properties have been valued in Asia and beyond, making it a well-respected plant over the years.

Traditional Chinese Medicine
In Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM), Stemona japonica, referred to as Bai Bu, is a valued medicinal plant.
Used primarily for its expectorant and antitussive properties, it forms a crucial component of treatments aimed at alleviating respiratory conditions.
TCM recognizes Bai Bu for its effectiveness in soothing coughs and expelling phlegm. The roots, known as Radix Stemonae, are the specific part of the plant employed for remedies.
Common Names and Descriptions
Stemona japonica, a member of the Stemona genus, stands apart with interesting descriptions. It’s known by various names across the regions including Chinese Stemona and Japanese Stemona, hinting at its widespread recognition in Asia.
A perennial herb, it’s defined by its tuberous roots; these roots are the primary repository of its medicinal traits.

Global Distribution
Stemona japonica extends beyond China, featuring across the Southeast Asia region, the Indian subcontinent, and even reaching Northern Australia.
Its cousins, Stemona tuberosa and Stemona sessilifolia, along with other Stemona species, flourish in this broad range.
Remote kin such as Stemona curtisii and Croomia heterosepala diversify the genus. The inclusion of multiple species within traditional practices spotlights the entire genus’s significance.
Stemona Japonica Benefits
Stemona japonica contains a diverse array of bioactive alkaloids, which serve as the foundation for its pharmacological activities.
Among these, stemofoline, stemonine, croomine, and tuberostemonine are significant for their roles in medicinal applications.
The Stemona alkaloids, notably, are the subject of considerable research due to their complex structures and challenging total syntheses.
1. Antitussive and Respiratory Benefits
The antitussive (cough-suppressing) properties of Stemona japonica are particularly notable. Compounds like stemofoline and neotuberostemonine help alleviate cough and are beneficial in the treatment of asthma.
The plant’s extracts act on the lungs, easing respiratory conditions, and have been used in traditional medicine to reduce pain associated with coughing.
2. Antimicrobial and Anticancer Properties
Stemona japonica’s pharmacology extends to its antimicrobial and anticancer properties. Stemonine and protostemonine have shown potential in combating microbial infections.
Furthermore, some alkaloids from the plant, such as maistemonine and stemospironine, are being investigated for their potential to inhibit cancer cell growth, attributing to Stemona japonica’s role in anti-inflammatory and anticancer research.
The traditional uses, phytochemistry, and pharmacology of Stemona species provide a more detailed insight into its secondary metabolites and the related pharmacological activities.
3. It’s Anti-inflammatory
Three new Stemona alkaloids, stemajapines A-C, were discovered from the roots of Stemona japonica, along with six known alkaloids; these compounds showed potential anti-inflammatory activity, suggesting a new direction for Stemona alkaloids beyond their traditional antitussive and insecticide properties.
4. Protects Lungs
A study investigated Stemona tuberosa’s (from the species Stemona – same as Stemona Japnica) effects on lung inflammation in mice exposed to cigarette smoke (CS).
Mice given Stemona tuberosa extract showed reduced inflammatory cells and chemicals in their lungs, suggesting it could be a helpful treatment for lung diseases like COPD.
The extract also protected lung tissue from damage caused by CS. These findings suggest that Stemona tuberosa might be a new and effective herb for treating lung diseases.
Cultivation and Ecology
In this section, you’ll learn about the specific characteristics of Stemona japonica as a perennial medicinal plant and its impact on the ecology where it thrives.
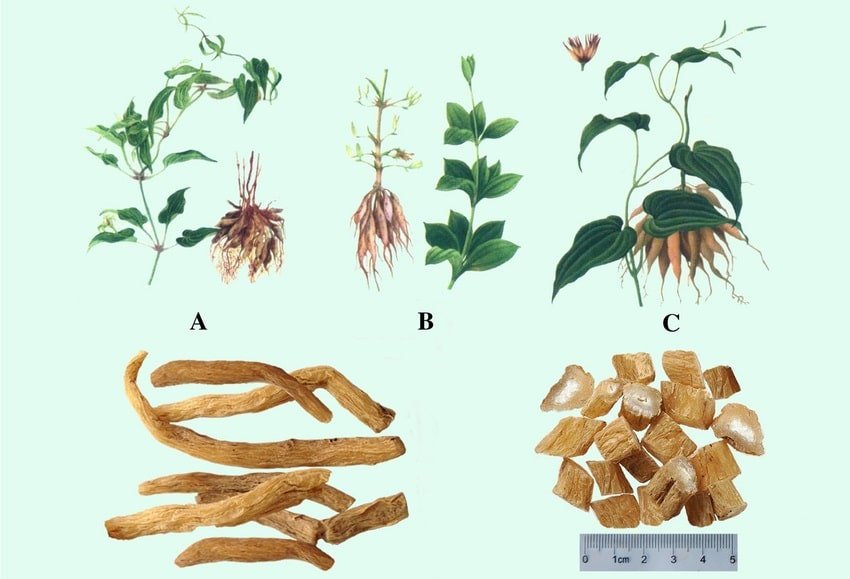
Plant Characteristics
Stemona japonica is a perennial herb known for its underground tubers and thin, climbing stems. Its leaves are arranged in an alternate pattern along the stem, often with a pale green hue.
As a part of the Stemona family, it is closely related to species like Stemona mairei and Stemona collinsae, sharing similar growth habits and uses in herbal medicine.
This plant exhibits a natural preference for moist, shaded environments, typically flourishing in the understory of forests.
Ecological Impact
On the ecological side, Stemona japonica plays a role in its native habitat by engaging with various pollinators and contributing to the biodiversity of the area.
Its presence can indicate the health of an ecosystem, especially since it thrives in undisturbed natural settings.
Additionally, extracts from Stemona japonica have been found to target the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor, making it a plant of significant interest for both its medicinal properties and its potential ecological interactions.
Chemical Insights
In this section, you’ll gain an understanding of the complex chemistry that makes Stemona japonica a plant of interest in traditional medicine and pharmacology, focusing on the chemical compounds known as stemona alkaloids and their synthesis.
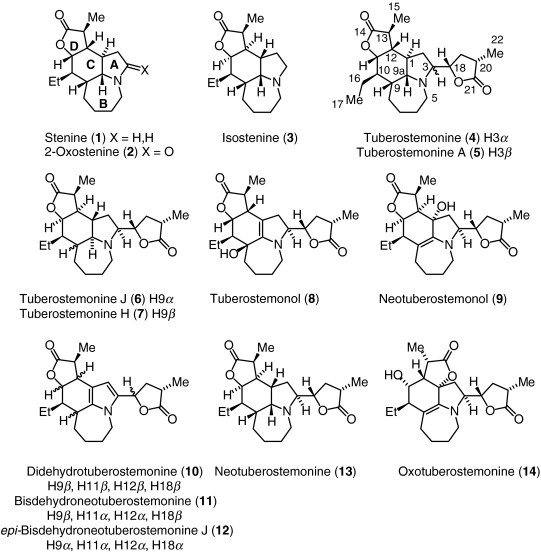
Analysis of Stemona Alkaloids
Stemona japonica is rich in bioactive compounds, primarily alkaloids and stilbenoids.
These substances are the driving force behind the plant’s medicinal value. Detailed NMR (nuclear magnetic resonance) studies have shown that stemona alkaloids often exhibit a distinct crystal structure that contributes to their biological activity.
For example, chemical investigations have revealed the presence of phenanthrenes, which are aromatic compounds believed to play a role in the therapeutic properties of the plant.
Stemona Alkaloid Synthesis
The total syntheses of stemona alkaloids is a significant area of research, given their potential applications.
Synthetic chemists aim to replicate these complex structures in the lab to allow for further study and potential drug development.
This process involves multiple steps, each carefully designed to introduce specific atoms into the chemical structure, resulting in the creation of a compound that mirrors those found in the natural plant.
Practical Applications and Safety
Stemona japonica is recognized for its potent insecticidal properties and is used in traditional remedies. When considering this plant for personal use, it’s essential to be aware of both its applications and the safety profile, including any potential toxicity.
Insecticidal Uses
Stemona japonica possesses active compounds that are effective in combating pests such as lice and Rhipicephalus microplus, a tick species.
These compounds have shown promising insecticidal and antifeedant activities. Your garden may benefit from the plant’s ability to deter unwelcome insects.
Additionally, extracts from Stemona japonica have been utilised as an insecticide in agricultural practices, protecting crops from various pests without the harsh environmental impact of synthetic chemicals.
Toxicity and Contraindications
While the insecticidal benefits of Stemona japonica are notable, it’s important to heed safety concerns. Inappropriate usage can lead to unwanted effects such as dryness in the mouth or diarrhea.
The plant’s toxicity levels are usually low, but it is crucial to use it correctly to avoid inflammation or other adverse reactions.
If you’re planning to use Stemona japonica as part of your wellness routine, consult with a healthcare provider, particularly if you’re currently experiencing health issues or are on medication, as the plant could exacerbate certain conditions.
Bottom Line
Stemona japonica, an important herb in traditional Chinese medicine, offers several pharmacological benefits. You’ll find that the active compounds in this plant, primarily Stemonae Radix, have been traditionally used to manage respiratory conditions and as an insecticide.
- Respiratory Health: It’s used as an antitussive to help relieve coughs.
- Anti-inflammatory: May reduce inflammation which is often a response to infection or injury.
- Antimicrobial: Has properties that are harmful to microorganisms.
- Anticancer: Early research indicates potential anti-cancer effects.
Exploration into the secondary metabolites from Stemona japonica has revealed a variety of pharmacological activities, including antiviral and antifeedant properties. These findings suggest that compounds in this plant have the potential to add value to medical treatments.
While past studies provide a basis for these uses, continued research is necessary to fully understand the scope and mechanism of action of Stemona japonica.
As such, your familiarity with the current state of knowledge should inform any decision-making regarding its use. The potential health benefits make it a plant of high interest within both scientific and medicinal communities.
Read Next
