Roman Chamomile Vs German Chamomile: What’s the difference?

I recently started writing about essential oils and I’ve come across the term “Roman Chamomile”. I immediately thought: “What is the difference between Roman Chamomile and German Chamomile?”
As it seems, chamomile (also called German Chamomile) and Roman Chamomile are two different species of plants that belong to the same family – the Asteraceae family.
While they share some similarities, there are also distinct differences between the two.
In this article, I am going to highlight all the differences between Chamomile and Roman Chamomile as well as answer any relevant questions about them.
Roman Chamomile Vs German Chamomile
Here’s a short video (2:40 min) from White Rabbit Institute of Healing YouTube channel for those of you who like videos.
Now, here’s a comprehensive table comparing the two types of Chamomile.
| FEATURE | CHAMOMILE | ROMAN CHAMOMILE |
|---|---|---|
| Common name | German chamomile, common chamomile | Roman chamomile, English chamomile |
| Scientific name | Matricaria recutita | Chamaemelum nobile |
| Native to | Europe, Asia, North Africa | Southern Europe, North Africa, Western Asia |
| Plant type | Annual | Perennial |
| Appearance | Several flowers on each stem, rounded central discs | Single flower on each stem, hollow central cone |
| Height | 20-60 cm | 15-30 cm |
| Stem | Hairy | Less hairy |
| Flower size | Larger, 1-2 cm | Smaller, up to 1 cm |
| Flower color | White with yellow center | White with yellow center |
| Leaf shape | Pinnate | More finely pinnate |
| Flower head base | Hollow | Filled with pith |
| Aromatic compound | Azulene | Esters |
| Essential oil color | Pale yellow to blue-green | Pale yellow |
| Aroma | Sweet, herbaceous, hay-like | Sweet, fruity, warm |
| Traditional uses | Tea, skin care, anxiety, insomnia | Tea, aromatherapy |
| Specific health benefits | More effective for treating inflammatory skin conditions. | More effective for digestive problems |
| Cold Tolerance | Zones 4 to 11 | Zones 4 to 9 |
Images
An image is like a thousands words – right? Here are side-by-side some interesting photo’s of both Roman Chamomile and German Chamomile.
Roman Chamomile (Chamaemelum nobile)



German Chamomile (Matricaria recutita)


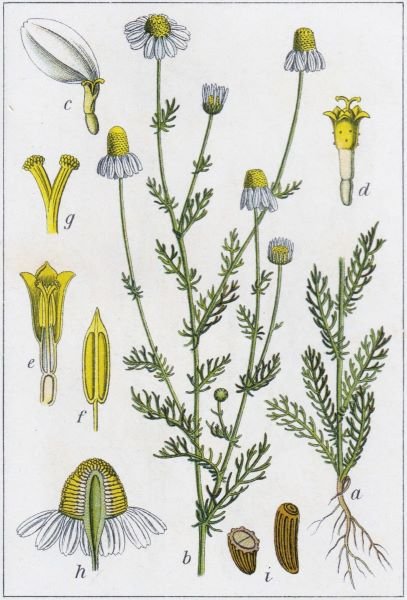
German Chamomile
- Chamomile, also known as German Chamomile or Matricaria chamomilla, is a flowering plant native to Europe and Western Asia.
- It is an annual plant that grows up to 2 feet tall and has feathery leaves and daisy-like flowers.
- Chamomile is widely known for its medicinal properties and is commonly used in herbal teas, essential oils, and skincare products.
- The flowers of chamomile contain various bioactive compounds, including chamazulene, apigenin, and bisabolol, which contribute to its anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and calming effects.
- Chamomile is often used to promote relaxation, relieve anxiety, aid digestion, and soothe skin irritations.
Roman Chamomile
- Roman Chamomile, also known as Chamaemelum nobile or English Chamomile, is a perennial plant native to Western Europe.
- It is a low-growing plant with small, daisy-like flowers and finely divided leaves.
- Roman Chamomile is also valued for its medicinal properties and is commonly used in herbal remedies, aromatherapy, and skincare products.
- The essential oil extracted from Roman Chamomile flowers contains various compounds, including esters, terpenes, and alcohols, which contribute to its anti-inflammatory, analgesic, and sedative effects.
- Roman Chamomile is often used to alleviate stress, promote sleep, relieve muscle pain, and soothe skin conditions.
Main Differences between Chamomile and Roman Chamomile:
- Species: Chamomile refers to the species Matricaria chamomilla, while Roman Chamomile refers to the species Chamaemelum nobile.
- Origin: Chamomile is native to Europe and Western Asia, while Roman Chamomile is native to Western Europe.
- Growth Habit: Chamomile is an annual plant that grows up to 2 feet tall, while Roman Chamomile is a perennial plant that has a low-growing habit.
- Appearance: Chamomile has feathery leaves and daisy-like flowers, while Roman Chamomile has finely divided leaves and small, daisy-like flowers.
- Chemical Composition: The bioactive compounds found in the flowers of chamomile and Roman Chamomile differ slightly, contributing to variations in their medicinal properties.
- Uses: While both chamomile and Roman Chamomile are used for their calming and soothing effects, they may have slightly different applications due to variations in their chemical composition.
The Asteraceae family
The Asteraceae family is one of the largest plant families, commonly known as the aster, daisy, or sunflower family.
It is a diverse family that includes over 23,000 species and encompasses a wide range of plants, including annuals, perennials, shrubs, and trees.
Members of the Asteraceae family are found in almost every habitat worldwide, from deserts to rainforests.
The family is characterized by its composite flower heads, which consist of many small individual flowers grouped together in a central disk surrounded by ray flowers. The flowers of the Asteraceae family are typically radially symmetrical and have a wide range of colors.
Many economically important plants belong to this family, including sunflowers, daisies, marigolds, chrysanthemums, as well as chamomile. Some members of the family, such as ragweed and dandelion, are considered weeds and can be problematic for agriculture and allergies.
The Asteraceae family is known for its medicinal properties, with several species used in traditional medicine for their anti-inflammatory, analgesic, and antimicrobial properties.
Frequently Asked Questions
Final Words
To summarize, chamomile and Roman Chamomile are two distinct species of plants that share some similarities but also have differences in their appearance, chemical composition, and uses.
Understanding these differences can help in choosing the appropriate variety for specific purposes, whether it be for herbal teas, skincare products, or medicinal remedies.
More Articles on Essential Oils
