What Are the Most Common Jarisch Herxheimer Reactions?

If you have been diagnosed with a bacterial infection, your doctor may prescribe antibiotics to help fight the infection.
However, in some cases, the use of antibiotics can cause a reaction known as the Jarisch-Herxheimer reaction. [1]
This reaction occurs when the bacteria that are being targeted by the antibiotics are killed off too quickly, causing the release of toxins into your bloodstream.
In this article I am presenting the most common Jarisch Herxheimer Reactions as well as more related information about this condition.
Throughout the article, you’ll find links to credible research papers and scientific articles (all links open in a new window). I encourage you to explore these resources for further study.
Understanding Jarisch Herxheimer Reactions
When you receive treatment for certain bacterial infections, you may experience a reaction known as the Jarisch Herxheimer reaction. This reaction is named after two dermatologists, Adolf Jarisch and Karl Herxheimer, who first described the phenomenon in patients with syphilis. [2]
The Jarisch Herxheimer reaction occurs when the antibiotics used to treat bacterial infections cause the bacteria to release toxins into your bloodstream faster than your body can eliminate them. This sudden release of toxins triggers an immune response, leading to symptoms such as fever, chills, headache, muscle pain, and skin rash. [3]
The reaction typically occurs within the first few hours or days of starting antibiotic treatment and usually lasts for a few hours to a few days. The severity of the reaction can vary from mild to severe, and in rare cases, it can be life-threatening.
The Jarisch Herxheimer reaction is most commonly associated with the treatment of syphilis, but it can also occur with other bacterial infections such as Lyme disease, leptospirosis, and relapsing fever. In addition, the reaction has been reported in patients with non-infectious conditions such as sarcoidosis and lupus. [3]
To manage the Jarisch Herxheimer reaction, your doctor may recommend taking over-the-counter pain relievers, such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen, to help relieve symptoms. In some cases, your doctor may also adjust your antibiotic dosage or switch to a different antibiotic to help reduce the severity of the reaction.
Overall, while the Jarisch Herxheimer reaction can be uncomfortable and sometimes alarming, it is generally a sign that your body is responding to the antibiotics and fighting off the infection. If you experience any symptoms of the reaction, be sure to contact your doctor right away to discuss the best course of action.
What Are the Most Common Jarisch Herxheimer Reactions?
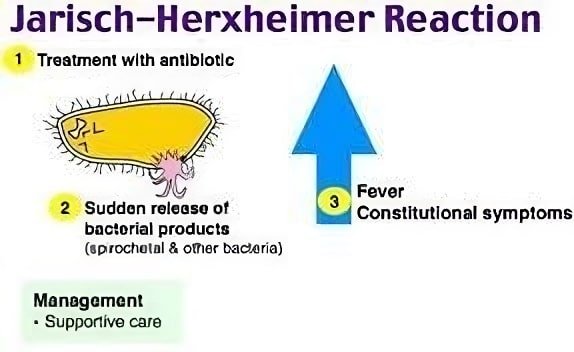
If you have been diagnosed with a bacterial infection such as syphilis, Lyme disease, or relapsing fever, your doctor may prescribe antibiotics to treat the infection.
However, you may experience a Jarisch Herxheimer reaction (JHR) after taking the antibiotics.
This reaction occurs when the bacteria in your body die off too quickly, releasing toxins into your bloodstream and causing an inflammatory response.
The symptoms of a JHR can vary depending on the type of infection being treated, the severity of the infection, and your overall health. Some common symptoms of a JHR include:
- Fever: You may experience a sudden increase in body temperature, which can be accompanied by chills and sweating.
- Headache: You may experience a throbbing headache that can be difficult to relieve.
- Muscle pain: You may experience muscle aches and pains, particularly in your arms and legs.
- Joint pain: You may experience joint pain, particularly in your knees and ankles.
- Skin rash: You may develop a rash on your skin, which can be itchy and uncomfortable.
- Nausea and vomiting: You may experience nausea and vomiting, which can be accompanied by diarrhea.
It is important to note that these symptoms can be mild or severe, depending on the individual. In rare cases, a JHR can be life-threatening, so it is important to seek medical attention if you experience any of these symptoms after taking antibiotics for a bacterial infection.
Your doctor may recommend taking over-the-counter pain relievers, such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen, to help relieve your symptoms. You may also be advised to drink plenty of fluids to help flush the toxins from your body.
JHR can be a challenging experience, but it is a sign that your body is fighting the infection. If you experience any symptoms of a JHR, it is important to seek medical attention and follow your doctor’s recommendations for treatment.
Timing and Duration of Reactions
The timing and duration of Jarisch-Herxheimer reactions can vary depending on the individual and the underlying condition being treated.
Generally, the reaction occurs within the first 24 hours after initiating treatment, but it can occur up to 72 hours after treatment has begun. [4]
The duration of the reaction can also vary, with symptoms lasting anywhere from a few hours to several days. In some cases, symptoms may persist for several weeks, but this is less common.
It is important to note that the severity of the reaction does not necessarily correlate with the severity of the underlying condition being treated.
In some cases, individuals with mild infections may experience more severe Jarisch-Herxheimer reactions than those with more severe infections.
Factors that may influence the timing and duration of Jarisch-Herxheimer reactions include the type and dose of medication being used, the individual’s overall health, and the presence of other underlying medical conditions.
If you experience a Jarisch-Herxheimer reaction, it is important to contact your healthcare provider. They may recommend adjusting your treatment regimen or providing supportive care to help manage your symptoms.
Management and Treatment
If you experience a Jarisch-Herxheimer reaction, it is important to seek medical attention immediately. Your doctor will likely recommend the following management and treatment options:
- Antibiotics: If you are being treated for a bacterial infection, your doctor may prescribe antibiotics to help fight the infection. Depending on the severity of your reaction, your doctor may adjust the dosage or switch to a different antibiotic.
- Pain relief: Over-the-counter pain relievers such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen may help alleviate symptoms such as fever, headache, and muscle aches. Your doctor may also prescribe stronger pain medication if necessary.
- Fluids: Drinking plenty of fluids can help prevent dehydration and help your body flush out the toxins released during the reaction.
- Rest: Resting and avoiding strenuous activity can help your body recover and reduce symptoms such as fatigue and weakness.
- Monitoring: If you are pregnant or have a pre-existing medical condition, your doctor may monitor you closely to ensure that the reaction does not cause any complications.
It is important to note that while a Jarisch-Herxheimer reaction can be uncomfortable, it is generally not life-threatening. Most people recover fully within a few days to a week. However, if you experience severe or persistent symptoms, it is important to seek medical attention immediately.
Implications for Chronic Diseases
If you have a chronic disease, you may be more susceptible to Jarisch-Herxheimer reactions.
In fact, some researchers suggest that chronic diseases may be a better model for natural endotoxin-associated disease than acute infections. [5]
One study found that patients with chronic Lyme disease had a higher incidence of Jarisch-Herxheimer reactions than patients with early Lyme disease. [6]
This suggests that the severity of the reaction may be related to the duration of the infection.
Another study found that patients with neurosyphilis are more likely to experience febrile reactions during the Jarisch-Herxheimer reaction when their cerebrospinal fluid contains an increased number of cells and protein. [4]
This suggests that the severity of the reaction may be related to the severity of the underlying disease.
Overall, if you have a chronic disease, it is important to be aware of the potential for Jarisch-Herxheimer reactions and to discuss this with your healthcare provider. They can help you manage any symptoms and ensure that you receive appropriate treatment.
Frequently Asked Questions
Bottom Line
To summarize, the Jarisch-Herxheimer reaction is a temporary response to antibiotic treatment of certain diseases. Common symptoms include fever, chills, headache, muscle aches, and skin rash.
It typically occurs within the first 24 hours of treatment and resolves within 72 hours. Severe cases can lead to complications such as low blood pressure and organ injury.
Medical supervision is crucial during treatment to manage potential reactions. Despite its intensity, the reaction is usually self-limiting and rarely fatal with proper care and management.
Read Next
