How to Repair Your DNA Naturally: The Science-Backed Protocol That Actually Works
Skip the expensive supplements and biohacks – here's what most recent research reveals about fixing damaged DNA through food, sleep, and simple lifestyle tweaks

Your DNA takes a beating every single day. We’re talking 19,000 hits of damage per cell, per day – that’s roughly one assault on your genetic code every five seconds [1].
This constant barrage comes from everything: the sun’s UV rays, pollution in your morning commute, that glass of wine at dinner, even the oxygen you breathe.
The damage adds up. Broken DNA strands accelerate aging, jack up your cancer risk, and mess with everything from your energy levels to how fast your hair turns gray. Scientists have linked DNA damage to over 200 diseases, including Alzheimer’s, diabetes, and heart disease [2].
But your body isn’t helpless. Built into every cell are sophisticated repair mechanisms that work 24/7 to fix genetic damage.
The problem?
Most of us unknowingly sabotage these systems through poor diet, chronic stress, and lifestyle choices that overwhelm our natural repair capacity.
This guide breaks down the latest research from 2023-2025 on natural DNA repair. You’ll learn which foods activate specific repair pathways, how exercise timing affects genetic recovery, and why certain supplements might be wasting your money.
No pseudoscience, no miracle cures – just evidence-based strategies that measurably reduce DNA damage markers in human studies.
We’ll cover the five major DNA repair systems your body uses, the foods that supercharge each one, lifestyle modifications that double repair rates, and how to create a personalized protocol based on your age and risk factors.
What is DNA Damage?
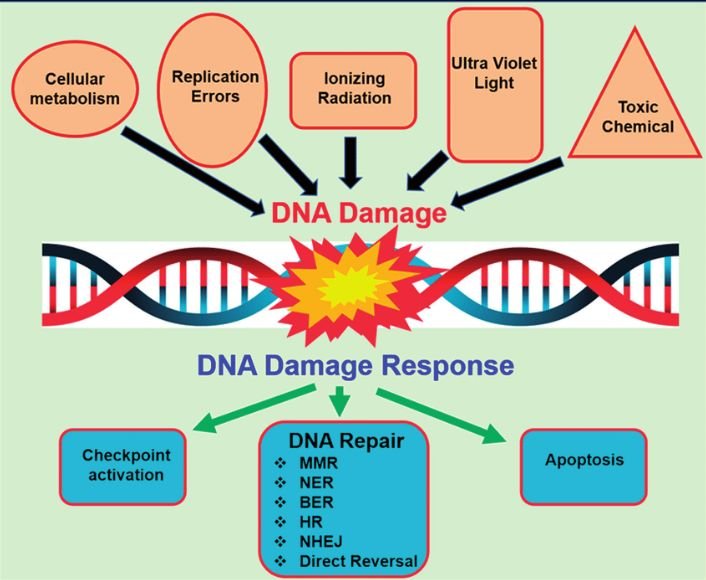
DNA damage = alterations to your genetic code that, if left unchecked, lead to mutations, cell death, or cancer.
Think of your DNA as a massive instruction manual for building and maintaining your body. Every time a page gets torn, smudged, or rewritten incorrectly, your cells struggle to follow the instructions properly.
The main culprits behind DNA damage include reactive oxygen species (basically, rogue oxygen molecules that act like molecular wrecking balls), UV radiation, environmental toxins like pesticides and air pollution, inflammatory foods, chronic stress hormones, and even normal metabolic processes.
Your cells generate DNA-damaging byproducts just from producing energy – it’s like your car’s engine creating exhaust fumes.
This damage directly drives aging. Researchers can now measure biological age by looking at DNA damage markers, and the correlation is stark: more damage equals faster aging at the cellular level [3].
Your Body’s Natural Repair Systems
Your cells run multiple DNA repair programs simultaneously, like having different specialized cleanup crews working around the clock. Understanding these systems helps you target them with specific nutrients and behaviors.
- Base Excision Repair (BER) handles the small stuff – single damaged bases in your DNA sequence. This system removes and replaces individual “letters” in your genetic code that get oxidized or chemically modified. BER depends heavily on zinc and magnesium to function, which explains why deficiencies in these minerals accelerate aging [4]. Think of BER as your genetic spellchecker, catching and fixing typos before they become permanent.
- Nucleotide Excision Repair (NER) tackles bigger problems, particularly UV damage from sun exposure. When UV light creates bulky lesions that distort the DNA helix, NER cuts out entire sections (about 30 nucleotides) and rebuilds them from scratch. This system requires vitamin D to work efficiently – one reason why vitamin D deficiency correlates with higher skin cancer rates [5]. NER is like replacing damaged sentences rather than just fixing individual letters.
- Mismatch Repair (MMR) catches errors that slip through during DNA replication. When cells divide, they sometimes insert the wrong nucleotide = genetic typo. MMR scans newly copied DNA and fixes these mistakes before they become permanent mutations. Folate and B12 are essential for this system, which is why pregnant women need extra folate to prevent birth defects [6].
- Homologous Recombination (HR) and Non-Homologous End Joining (NHEJ) repair the worst type of damage: double-strand breaks where both sides of the DNA ladder snap. HR uses a backup copy of the DNA as a template for accurate repair, while NHEJ quickly glues the broken ends back together – sometimes introducing errors in the process. BRCA genes, famous for their role in breast cancer, are actually HR repair genes. When they malfunction, double-strand breaks accumulate, drastically increasing cancer risk [7].
- Telomerase Activity doesn’t repair damage per se, but maintains the protective caps (telomeres) at the end of chromosomes. Every time a cell divides, telomeres get shorter. When they’re gone, the cell dies or becomes senescent = zombie cell that causes inflammation. Certain foods and lifestyle factors can boost telomerase activity, essentially slowing your cellular aging clock [8].
The Ultimate DNA Repair Food Arsenal

Powerhouse Fruits for DNA Protection
Wild Bluberies
Wild blueberries aren’t just regular blueberries with better marketing.
They contain twice the anthocyanin content of cultivated varieties, and human studies show they reduce DNA damage by 20% in just 4-6 weeks of daily consumption [9].
The key? Eating them raw and fresh, as cooking destroys up to 60% of their DNA-protective compounds. One cup daily provides measurable protection against oxidative DNA damage.
Kiwis
Kiwi fruits pack a weird DNA repair punch that surprised researchers. Three kiwis daily significantly increased DNA repair capacity in human lymphocytes within 24 hours [10].
The effect peaks at three fruits – eating more doesn’t provide additional benefit. Golden kiwis work slightly better than green ones, probably due to higher vitamin C content.
(Ed. note: The fuzzy skin is edible and contains additional antioxidants, though most people prefer to peel them.)
Citrus Fruits
Citrus fruits deliver naringenin, a flavonoid that specifically enhances DNA repair in prostate cells. Grapefruit contains the highest levels, followed by oranges and lemons [11].
The white pith – that bitter stuff most people remove – contains the highest concentration. Yeah, it tastes like cardboard, but it’s where the DNA protection lives.
Strawberries / Respberries
Strawberries and raspberries offer ellagic acid, which activates multiple DNA repair pathways simultaneously. Fresh berries beat frozen for DNA protection, though frozen still provides benefit.
A 2024 study found that people eating 2 cups of mixed berries daily showed 15% less DNA damage after six weeks [12].
Pomegranates
Pomegranates earned their superfood status legitimately. The juice increases DNA repair enzyme activity by up to 30% in human studies [13].
But here’s the catch: commercial pomegranate juice often contains added sugars that create oxidative stress, partially canceling out the benefits. Fresh arils or pure, unsweetened juice work best.
DNA-Repairing Vegetables
Cruciferous vegetables = DNA repair powerhouses. Broccoli sprouts contain 50 times more sulforaphane than mature broccoli, and sulforaphane directly activates NER and BER repair pathways [14].
Three-day-old sprouts hit the sweet spot for maximum sulforaphane content. You can grow them on your kitchen counter for pennies.
Raw broccoli, cauliflower, and Brussels sprouts also boost DNA repair, but cooking method matters massively. Steaming for under 5 minutes preserves most benefits.
Boiling? Forget it – you’ll lose 70% of the DNA-protective compounds in the cooking water [15].
PRO TIP: Microwaving actually preserves more nutrients than most cooking methods, despite what your health-conscious friend claims.
Watercress deserves more respect. A single serving (80g) reduced DNA damage by 24% in smokers – people with extremely high oxidative stress [16].
It works within hours of consumption, making it ideal for protecting against acute stressors like air travel or intense exercise.
Leafy greens provide folate, essential for DNA synthesis and repair. But synthetic folic acid in supplements doesn’t work the same as natural folate from food.
Spinach, arugula, and Swiss chard deliver the real deal, plus hundreds of other protective compounds [17].
Dark leafy greens also contain chlorophyll, which binds to carcinogens and prevents them from damaging DNA in the first place.
Carrots and sweet potatoes supply beta-cryptoxanthin, a carotenoid that specifically protects lung tissue DNA from damage [18].
Cooking actually increases bioavailability – your body absorbs 5 times more beta-carotene from cooked carrots than raw ones. Add a bit of fat (olive oil, nuts) to boost absorption even further.
Superfoods and Specialty Items
Honey
Raw honey contains over 200,000 phytochemical compounds, many of which protect and repair DNA [19]. Not all honey is equal though. Manuka honey shows the strongest DNA-protective effects, followed by buckwheat and wildflower varieties.
Commercial processed honey? Basically sugar water with minimal benefits.
Spirulina
Spirulina’s amino acid profile closely matches what your DNA and RNA need for repair and replication. This blue-green algae reduced DNA damage markers by 30% in people exposed to radiation [20].
The taste takes getting used to – mixing it into smoothies masks the pond-water flavor.
Wild Mushrooms
Wild mushrooms provide nucleotides, the building blocks for DNA repair. Shiitake, maitake, and reishi mushrooms show the strongest effects [21].
Store-bought button mushrooms? Not so much. The DNA-protective compounds concentrate in wild or specialty varieties that produce more defensive chemicals against environmental stress.
Brazil Nuts
Brazil nuts remain the selenium champion. Just two nuts daily provide enough selenium to activate glutathione peroxidase, a crucial DNA repair enzyme [22].
But don’t go nuts on the nuts – too much selenium becomes toxic. Two Brazil nuts daily, max.
Raw nuts and seeds supply nucleic acids that support DNA synthesis and repair. Pumpkin seeds, sunflower seeds, and walnuts show the strongest benefits [23].
Roasting reduces DNA-protective compounds by about 20%, so raw or lightly toasted works best.
Herbs and Natural Compounds
Nettle might seem like a weird DNA protector – it’s literally a weed that stings you. But nettle tea supports DNA repair through multiple mechanisms: blood cleansing, heavy metal chelation, and providing minerals essential for repair enzymes [24]. Fresh nettle tea beats dried, if you can find it (or brave picking it yourself with gloves).

Green tea’s EGCG = one of the most studied DNA-protective compounds. Three cups daily reduced DNA damage by 20% in multiple studies [25].
Matcha provides 10 times more EGCG than regular green tea, since you consume the whole leaf. The first brew contains the most DNA-protective compounds – reusing tea bags dilutes the benefits.
Turmeric’s curcumin maintains genetic integrity through multiple pathways, but absorption sucks without black pepper. Adding just 1/20th teaspoon of black pepper increases curcumin absorption by 2000% [26]. Fresh turmeric root contains oils that improve absorption naturally, making it superior to powdered supplements.
Xanthohumol from hops (yes, beer hops) reduced DNA damage by 33% in a clinical trial [27]. Before you crack open a cold one, know that beer processing destroys most xanthohumol. Hop extract supplements or alcohol-free hop teas provide the benefits without the DNA-damaging alcohol.
Chlorophyllin, the water-soluble form of chlorophyll, provides multi-targeted DNA protection. It binds to carcinogens, boosts DNA repair enzymes, and acts as an antioxidant [28]. Liquid chlorophyll drops added to water throughout the day provide consistent protection.
Lifestyle Strategies for Maximum DNA Repair
Exercise Protocols for DNA Health
Exercise creates a DNA paradox: it temporarily increases oxidative stress and DNA damage, but ultimately strengthens repair mechanisms. The key lies in finding the sweet spot between too little and too much.
Moderate exercise for 30 minutes, five times per week, optimally activates DNA repair without overwhelming the system [29]. A 16-week study found this protocol reduced DNA damage markers by 15% while improving repair enzyme activity by 20%. The magic happens during recovery, not during exercise itself.
Cardiovascular exercise and strength training affect DNA differently. Cardio boosts mitochondrial DNA repair and increases production of antioxidant enzymes. Strength training activates growth factors that protect nuclear DNA and maintain telomere length [30]. Combining both provides comprehensive DNA protection.
Here’s what most fitness influencers won’t tell you: exhaustive exercise hammers your DNA. Marathon runners show elevated DNA damage markers for up to 72 hours post-race [31]. Weekend warriors who go from couch to CrossFit create oxidative storms their repair systems can’t handle. Build intensity gradually – your DNA will thank you.
The timing matters too. Morning exercise aligns with natural cortisol rhythms and allows DNA repair to occur during sleep. Evening exercise can disrupt sleep quality, reducing the crucial repair window [32].
Sleep Optimization for DNA Repair
Sleep isn’t just rest – it’s when your DNA repair crew works overtime. Chromosomal activity peaks between 2-4 AM, with certain repair genes increasing expression by 500% during deep sleep [33].

Seven to eight hours nightly maintains optimal DNA repair capacity. Less than six hours causes measurable increases in DNA damage within a week. A single night of sleep deprivation disrupts over 700 genes, including many involved in DNA repair [34].
Quality beats quantity for DNA repair. Deep sleep (stages 3-4) drives the most repair activity. Room temperature between 65-68°F, complete darkness, and consistent sleep-wake times maximize deep sleep percentage. Blue light exposure after sunset reduces repair enzyme production by up to 40% [35].
“I’m a night owl, though.” – you might say..
Your chronotype does matter, but fighting your natural circadian rhythm creates additional stress on DNA repair systems. Work with your body clock, not against it, but still aim for 7-8 hours regardless of when you sleep.
Melatonin, your body’s sleep hormone, directly participates in DNA repair beyond just making you drowsy. It scavenges free radicals, activates repair enzymes, and protects mitochondrial DNA [36]. Tart cherry juice naturally boosts melatonin without the grogginess of supplements.
Stress Management Techniques
Chronic stress absolutely demolishes DNA integrity. Cortisol, your primary stress hormone, shortens telomeres and impairs multiple repair pathways [37]. People with high chronic stress show DNA damage equivalent to being 10 years older biologically.
Meditation measurably increases telomerase activity – the enzyme that rebuilds telomeres. Just 12 minutes daily of focused meditation increased telomerase by 30% after two months [38]. You don’t need to sit in lotus position chanting “om” – guided meditation apps work just as well.
The 4-7-8 breathing technique provides immediate DNA protection during acute stress. Breathe in for 4 counts, hold for 7, exhale for 8. This activates the parasympathetic nervous system, reducing cortisol and oxidative stress within minutes [39]. Use it before stressful meetings, during traffic, or whenever you feel tension building.
Social connection buffers against stress-induced DNA damage. People with strong social networks show 50% less telomere shortening compared to isolated individuals [40]. Regular social interaction – even brief positive encounters – provides measurable DNA protection.
Environmental Toxin Avoidance
UV radiation remains the number one environmental DNA destroyer. Daily sunscreen use (SPF 30+) prevents up to 80% of UV-induced DNA damage [41]. Apply it every morning, even if you’re mostly indoors – UV penetrates windows.
Smoking creates an aldehyde apocalypse in your DNA. One cigarette generates enough aldehydes to cause 1,000 DNA breaks [42]. Secondhand smoke causes similar damage. Vaping? Still produces DNA-damaging compounds, though potentially less than cigarettes.

Air quality dramatically impacts DNA integrity. Indoor air often contains 2-5 times more pollutants than outdoor air [43]. HEPA filters, houseplants, and regular ventilation reduce indoor DNA damage. On high pollution days, exercise indoors and limit outdoor exposure.
Household chemicals and personal care products contribute to daily DNA assault. Phthalates, parabens, and synthetic fragrances all show DNA-damaging effects [44]. Switch to fragrance-free, natural products when possible. Your DNA doesn’t care if your laundry smells like “mountain breeze.”
Natural Supplements for DNA Repair

Essential Nutrients
- Vitamin D functions as a DNA repair hormone, not just a vitamin. It directly activates genes involved in DNA repair while suppressing inflammation that causes damage [45]. Most people need 2000-4000 IU daily to maintain optimal levels for DNA protection. Get tested – over 40% of adults are deficient.
- Folate and B12 work together in DNA methylation and synthesis. But here’s the kicker: synthetic folic acid can mask B12 deficiency while allowing DNA damage to accumulate [46]. Methylfolate (the active form) plus methylcobalamin (active B12) provide superior DNA support compared to standard supplements.
- Selenium activates glutathione peroxidase and other DNA repair enzymes, but the form matters. Selenomethionine from Brazil nuts shows superior bioavailability compared to sodium selenite in supplements [47]. Two Brazil nuts daily beats any selenium pill.
- Vitamin E protects DNA from lipid peroxidation, but most supplements contain only alpha-tocopherol. Mixed tocopherols and tocotrienols (the full vitamin E complex) provide comprehensive DNA protection [48]. Food sources like sunflower seeds deliver the complete package.
- Zinc powers over 300 enzymes, including crucial DNA repair proteins. Deficiency immediately impairs DNA repair capacity [49]. 15-20mg daily from food or supplements maintains repair function, but more isn’t better – excess zinc interferes with copper absorption, creating different problems.
Advanced Compounds
- NAD+ precursors like NMN (nicotinamide mononucleotide) boost cellular repair by increasing NAD+ levels. NAD+ naturally declines with age, reducing DNA repair efficiency [50]. Studies show 250-500mg NMN daily increases DNA repair markers within weeks, though it’ll cost you $50-100 monthly. If you’re looking for NMN supplements feel free to check the top 10 here.
- AC-11, derived from cat’s claw, clinically lengthened telomeres in human studies. 350mg daily for two months increased telomere length by an average of 7% [51]. It also enhanced DNA repair capacity in people exposed to UV radiation.
- Astragalus root contains cycloastragenol, which activates telomerase. Traditional Chinese medicine has used it for millennia, but modern research confirms its DNA-protective effects [52]. 500-1000mg of standardized extract provides benefits without the side effects of synthetic telomerase activators.
- Alpha-lipoic acid regenerates other antioxidants and directly supports mitochondrial DNA repair. 300-600mg daily reduces oxidative DNA damage markers [53]. Take it on an empty stomach – food reduces absorption by up to 60%.
PRO TIP: Dosing matters with all supplements. Start low, increase gradually, and monitor how you feel. More doesn’t equal better – excessive antioxidants can actually impair your body’s natural repair responses.
Age and Gender-Specific Strategies
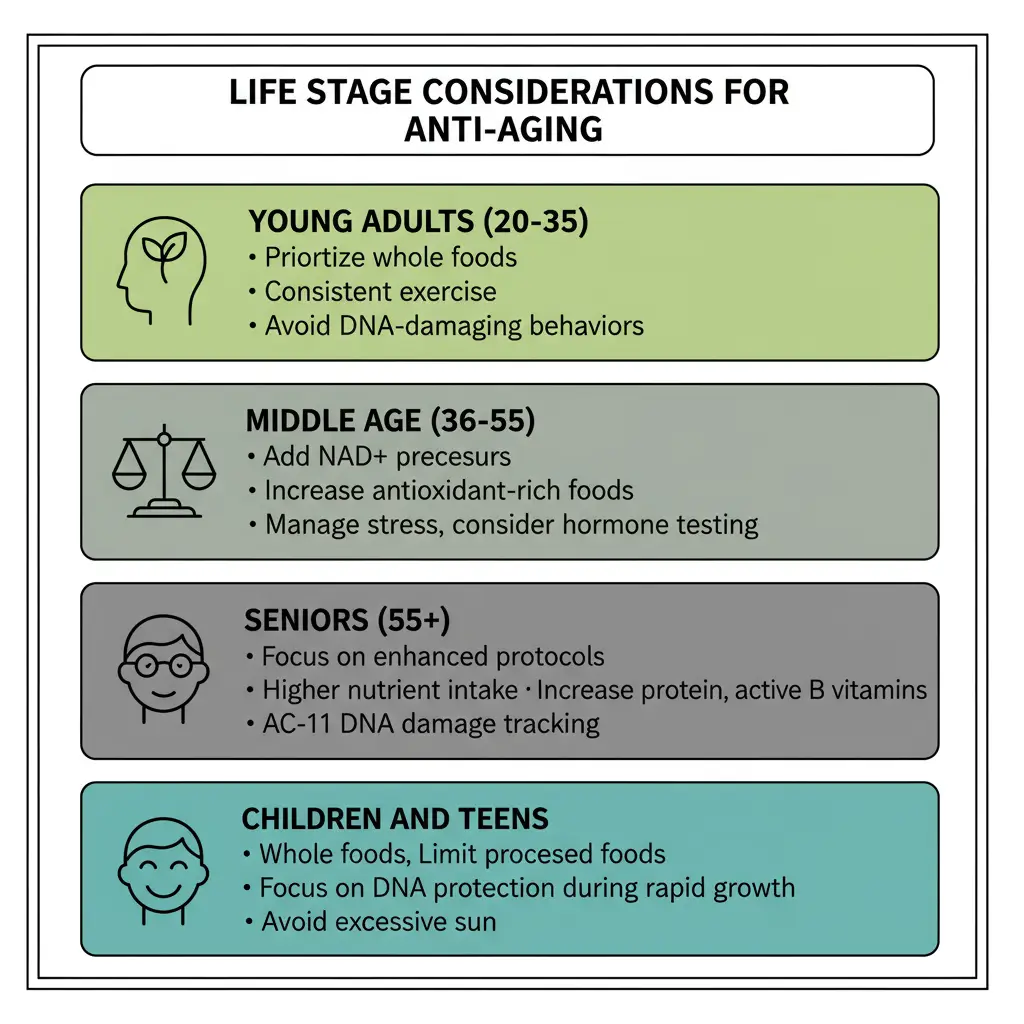
Life Stage Considerations
- Young adults (20-35) should focus on prevention and building robust repair systems. Your DNA repair capacity peaks during these years, so establishing protective habits now pays massive dividends later. Prioritize whole foods over supplements, maintain consistent exercise, and avoid DNA-damaging behaviors like binge drinking and tanning beds. Your telomeres are still long – keep them that way.
- Middle age (36-55) requires active repair strategies as DNA damage accumulates and repair efficiency declines. Add targeted supplements like NAD+ precursors, increase antioxidant-rich foods, and manage stress religiously. Hormone changes affect DNA repair – consider testing hormone levels if you notice accelerated aging signs. This is when DNA damage starts manifesting as visible aging and disease risk.
- Seniors (55+) need enhanced protocols to compensate for declining repair capacity. Multiple DNA repair systems slow down with age, requiring higher nutrient intake for the same protection [54]. Increase protein for DNA synthesis, supplement with active forms of B vitamins, and consider advanced compounds like AC-11. Regular testing of inflammatory markers helps track DNA damage levels.
- Children and teens require different DNA protection strategies due to rapid growth and development. Their cells divide frequently, making DNA integrity crucial. Focus on whole foods rather than supplements, limit processed foods that cause oxidative stress, and establish healthy sleep habits early. Excessive sun exposure during youth dramatically increases lifetime DNA damage accumulation [55].
Gender-Specific Factors
- Women’s estrogen provides natural DNA protection – until menopause. Estrogen activates DNA repair genes and maintains telomere length [56]. Post-menopause, DNA damage accelerates without hormone replacement. Phytoestrogens from soy, flax, and legumes provide mild protective effects. Women also need more folate due to menstruation and potential pregnancy.
- Men have higher baseline DNA damage due to testosterone’s pro-oxidant effects, but testosterone also supports certain repair mechanisms [57]. Low testosterone correlates with increased DNA damage and shortened telomeres. Zinc and vitamin D are particularly important for men’s DNA health, as they support both testosterone production and DNA repair.
- Pregnancy and breastfeeding create unique DNA challenges. The developing fetus requires massive amounts of folate, B12, and other nutrients for DNA synthesis. Maternal DNA damage can affect fetal development [58]. Prenatal vitamins are non-negotiable, but whole foods provide additional protective compounds not found in pills.
TIP: Hormonal fluctuations throughout life affect DNA repair capacity. Birth control pills, hormone replacement therapy, and natural hormone changes all impact DNA integrity. Track your cycle (if applicable) and notice when you feel most resilient – that’s when your DNA repair is likely optimal.
Creating Your Personal DNA Repair Protocol

Daily Routine Template
Morning sets the DNA protection tone for your entire day.
- Start with 16oz of water with liquid chlorophyll upon waking – this helps flush overnight metabolic waste that damages DNA.
- Take vitamin D and B-complex with breakfast for optimal absorption.
- Include DNA-protective foods: berries with breakfast, green tea instead of coffee (or alongside it).
- Exercise timing depends on your schedule, but consistency matters more than perfection. 30 minutes of moderate cardio or 20 minutes of strength training, ideally in the morning when cortisol naturally peaks.
- Post-workout, consume vitamin C-rich foods to neutralize exercise-induced oxidative stress.
Midday strategies focus on stress management and continued protection.
- Practice the 4-7-8 breathing technique before meals to activate parasympathetic DNA repair.
- Apply sunscreen before going outside, even for brief exposures.
- Include cruciferous vegetables with lunch – raw broccoli sprouts in sandwiches or salads work great.
Evening routine prepares your body for overnight DNA repair.
- Finish eating 3 hours before bed to allow DNA repair systems to focus on maintenance rather than digestion.
- Dim lights after sunset to support melatonin production.
- Take magnesium glycinate (200-400mg) before bed to support overnight repair processes.
30-Day Meal Planning Guide
Weeks 1-2 establish the foundation with easily accessible DNA-protective foods. Every meal includes at least two DNA-supporting ingredients.
- Breakfast: overnight oats with berries and walnuts.
- Lunch: large salad with watercress, carrots, and pumpkin seeds.
- Dinner: wild salmon with steamed broccoli and sweet potato. Snacks: apple slices with almond butter, or carrot sticks with hummus.
Weeks 3-4 integrate advanced strategies and superfoods. Add spirulina to morning smoothies, incorporate medicinal mushrooms into soups, drink nettle tea in the afternoon. Experiment with less common DNA protectors: pomegranate arils on salads, Brazil nuts as afternoon snacks, turmeric-ginger shots before dinner.
Sample daily menu for maximum DNA protection:
- Breakfast – wild blueberry smoothie with spinach, banana, spirulina, and ground flax.
- Mid-morning – green tea with raw honey.
- Lunch – quinoa bowl with roasted vegetables, chickpeas, and tahini dressing.
- Afternoon – 2 Brazil nuts and an orange.
- Dinner – miso soup with shiitake mushrooms, followed by wild salmon, sautéed kale, and purple sweet potato.
- Evening – tart cherry juice mixed with sparkling water.
Shopping lists organized by season maximize nutrient density and affordability.
- Spring: asparagus, artichokes, strawberries.
- Summer: tomatoes, watermelon, peaches.
- Fall: Brussels sprouts, pomegranates, persimmons.
- Winter: citrus fruits, root vegetables, winter squash.
PRO TIP: Frozen organic berries provide year-round DNA protection when fresh isn’t available.
Troubleshooting Common Challenges
Budget constraints don’t excuse DNA damage.
- Frozen vegetables retain most DNA-protective compounds and cost fraction of fresh.
- Eggs provide complete protein and choline for DNA methylation at $3/dozen.
- Dried beans and lentils offer folate and fiber for under $2/pound.
- Grow your own broccoli sprouts for $1/week.
Time limitations require strategic planning.
- Batch cook DNA-protective meals on weekends.
- Prep vegetables immediately after shopping.
- Keep emergency DNA-support snacks available: nuts, seeds, dried fruit.
Dietary restrictions need creative adaptations.
- Vegans should supplement B12 and possibly zinc.
- Keto dieters can focus on low-carb DNA protectors: leafy greens, avocados, nuts.
- Gluten-free isn’t a barrier – most DNA-protective foods are naturally gluten-free.
- Food allergies require substitutions but don’t prevent DNA protection.
Measuring Your Progress
Biomarkers and Testing
Telomere length testing provides direct measurement of cellular aging and DNA protection effectiveness. Commercial tests run $100-300 and measure average telomere length in white blood cells [59]. Test initially for baseline, then every 6-12 months to track progress. Improvements take time – expect 3-6 months before seeing measurable changes.
Oxidative stress markers indicate ongoing DNA damage. 8-hydroxy-2-deoxyguanosine (8-OHdG) in urine directly reflects DNA oxidative damage [60]. F2-isoprostanes measure lipid peroxidation that damages cellular membranes and DNA. These tests run $150-400 but provide objective data on your DNA damage levels.
Inflammatory markers correlate with DNA damage and repair capacity. C-reactive protein (CRP) and homocysteine are affordable tests ($30-50) available through most doctors [61]. Elevated levels indicate ongoing DNA damage and increased disease risk. Track these quarterly to monitor protocol effectiveness.
Timing matters for testing accuracy. Test in the morning after fasting for consistent results. Avoid testing within 48 hours of intense exercise or acute stress, which temporarily elevate markers. Seasonal variations exist – DNA damage markers typically peak in winter due to less sun exposure and vitamin D production.
Subjective Indicators
Energy levels reflect mitochondrial DNA health. Sustained energy throughout the day, without afternoon crashes, indicates improving mitochondrial function. Most people notice energy improvements within 2-3 weeks of starting a DNA repair protocol.
Sleep quality improvements suggest enhanced overnight DNA repair. Deeper sleep, easier wake-ups, and feeling refreshed indicate your repair systems are working efficiently. Dreams often become more vivid as REM sleep quality improves.
Stress resilience increases as DNA repair capacity improves. You’ll notice faster recovery from stressful events, less anxiety about daily challenges, and improved emotional regulation. This creates a positive feedback loop – less stress means less DNA damage.
Physical appearance changes reflect cellular DNA health. Skin becomes clearer and more radiant (usually noticeable after 6-8 weeks), hair grows faster and stronger, and nails become less brittle. These external changes mirror internal DNA repair improvements.
FAQs
Conclusion
Your DNA takes 19,000 hits daily, but you’re not defenseless. The evidence is clear: specific foods, lifestyle modifications, and targeted supplements measurably reduce DNA damage and boost repair capacity. You don’t need expensive biohacks or extreme protocols – just consistent application of science-backed strategies.
Start with the basics: add 2 cups of berries daily, practice 12 minutes of meditation, get 7-8 hours of sleep, and take a vitamin D supplement if you’re deficient. These four changes alone can reduce DNA damage markers by 20-30% within two months.
DNA repair isn’t a quick fix – it’s a lifestyle investment that compounds over time. Every day you protect your DNA, you’re literally preserving your genetic blueprint for future years. The earlier you start, the more benefit you’ll accumulate.
Next steps: Pick three DNA-protective foods to add this week. Download a meditation app and commit to 10 minutes daily. Test your vitamin D levels. Small, consistent actions create massive long-term DNA protection.
Your genes aren’t your destiny – they’re your responsibility. The tools exist, the science is solid, and your DNA repair systems are waiting to be activated. What you do today determines how your genes express tomorrow.

