How does hyperbaric oxygen therapy work for wound healing?
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy, or HBOT, is a medical treatment that is used to treat a variety of conditions, including wound healing. The treatment involves breathing pure oxygen in a pressurized chamber, which increases the amount of oxygen in the blood.
This increased oxygen flow helps to stimulate the growth of new blood vessels and tissue, promoting faster and more effective wound healing.
In this article, we will explore the science behind how HBOT works, the types of wounds that can be treated with this therapy, and the potential risks and side effects. We will also discuss the importance of discussing HBOT as a treatment option with a healthcare professional.
What is HBOT and how it is used to treat wounds?
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) is a medical treatment that involves breathing pure oxygen in a pressurized chamber. The pressure inside the chamber is increased to a level higher than the normal atmospheric pressure, which allows the lungs to absorb more oxygen than it would at normal pressure.
This increased oxygen flow helps to stimulate the growth of new blood vessels and tissue, promoting faster and more effective wound healing.
HBOT is used to treat a variety of conditions, including wounds that are slow to heal due to poor circulation, infection, or tissue damage. It can also be used to treat certain types of infections, such as gas gangrene and osteomyelitis, and to enhance the healing of burns and skin grafts. HBOT is also used to treat carbon monoxide poisoning and decompression sickness.
The treatment is typically administered in a hyperbaric chamber, which is a sealed chamber that can be pressurized. The patient lies on a bed inside the chamber and breathes pure oxygen through a mask or hood.
The treatment typically lasts for one to two hours and is typically administered on an outpatient basis. The number of treatments and the duration of treatment vary depending on the condition being treated and the response of the patient.
Related: How to Choose the Best Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy Chamber
What is the science behind HBOT’s wound healing properties?
HBOT promotes wound healing by increasing the amount of oxygen in the blood. When a person is in a hyperbaric chamber and the pressure is increased, the lungs can absorb more oxygen than it would at normal pressure.
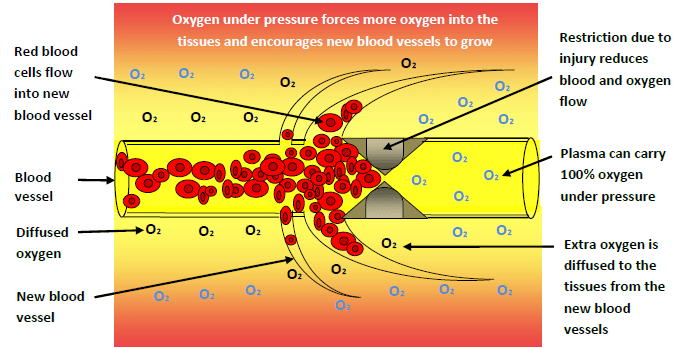
This increased oxygen flow is then transported throughout the body, including to the wound site. The increased oxygen helps to stimulate the growth of new blood vessels, which is essential for the healing process.
The increased oxygen also helps to fight off infection and promotes the growth of new tissue. This is because oxygen is essential for the process of cell growth and repair.
When there is an adequate supply of oxygen, the cells in the wound can divide and multiply more quickly, resulting in faster wound healing.
Additionally, the pressurized environment in the hyperbaric chamber helps to reduce inflammation and swelling, which can also aid in the healing process. The pressure also helps to push out any trapped gases such as carbon monoxide and nitrogen that might be interfering with the healing process.
KEY TAKEAWAY
Overall, the increased oxygen supply provided by HBOT helps to promote wound healing by stimulating the growth of new blood vessels and tissue, fighting off infection, and reducing inflammation and swelling.
What types of wounds that can be treated with HBOT?
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) can be used to treat a variety of wounds, including:
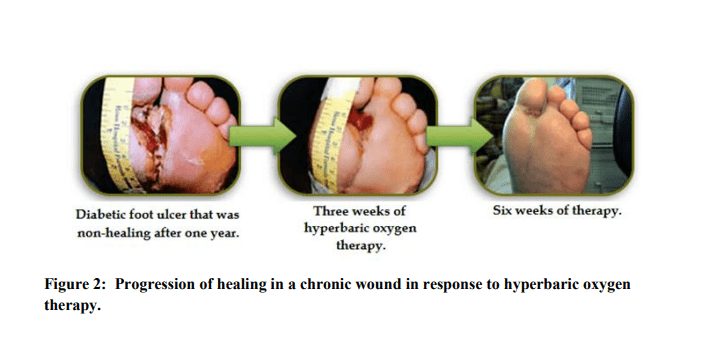
- Diabetic foot ulcers: These are common in people with diabetes and occur as a result of poor circulation and nerve damage. HBOT can help to increase blood flow to the wound, promoting faster healing and reducing the risk of amputation.
- Pressure sores: These are caused by prolonged pressure on one area of the body, such as in people who are bedridden or use a wheelchair. HBOT can help to increase blood flow to the wound, promoting faster healing and reducing the risk of infection.
- Crush injuries: These are caused by a traumatic injury that results in tissue damage and poor blood flow to the affected area. HBOT can help to increase blood flow to the wound, promoting faster healing and reducing the risk of infection.
- Soft tissue injuries: These are injuries to muscles, tendons, and ligaments, HBOT can help to reduce pain, swelling, and inflammation, promoting faster healing.
What are some potential potential risks and side effects of HBOT treatment?
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) is generally considered to be a safe treatment, but like all medical treatments, it does have some potential risks and side effects. Some of the most common side effects of HBOT include:
- Ear and sinus pain: The change in pressure inside the hyperbaric chamber can cause pain in the ears and sinuses. This can be managed by equalizing the pressure in the ears and sinuses by swallowing, yawning or performing a valsalva maneuver.
- Fatigue: Some people may feel tired after a treatment session. This is usually temporary and can be managed by getting adequate rest.
- Dizziness: Some people may feel dizzy after a treatment session. This is usually temporary and can be managed by getting adequate rest.
- Nausea: Some people may feel nauseous after a treatment session. This is usually temporary and can be managed by getting adequate rest.
- Shortness of breath: Some people may feel short of breath after a treatment session. This is usually temporary and can be managed by getting adequate rest.
- Transient myopia: Some people may experience temporary nearsightedness after a treatment session. This is usually temporary and vision typically returns to normal within 24 hours.
- Aseptic Osteomyelitis : HBOT may rarely cause aseptic osteomyelitis, a condition caused by inflammation of the bone without infection.
- Barotrauma: this is a condition caused by mechanical injury to body tissues due to pressure changes. It can occur in the middle ear, lungs, or sinuses.
Some of these risks can be mitigated by properly preparing for the treatment, such as avoiding caffeine and nicotine before the treatment, and by properly managing the side effects. Consult your healthcare professional if you experience any persistent or severe side effects.

Bottom Line
In conclusion, Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy (HBOT) is a medical treatment that involves breathing pure oxygen in a pressurized chamber and it is used to treat a variety of conditions, including wound healing.
HBOT works by increasing the amount of oxygen in the blood, which helps to stimulate the growth of new blood vessels and tissue, promoting faster and more effective wound healing.
The conditions that can be treated with HBOT include diabetic foot ulcers, pressure sores, crush injuries, soft tissue injuries, carbon monoxide poisoning, decompression sickness and many more.
The treatment typically administered in a hyperbaric chamber, which is a sealed chamber that can be pressurized and the patient lies on a bed inside the chamber and breathes pure oxygen through a mask or hood.
HBOT is a safe, non-invasive and effective treatment option for many conditions, including wound healing, but it also has some potential risks and side effects such as ear and sinus pain, fatigue, dizziness, nausea, shortness of breath, transient myopia and aseptic osteomyelitis.
Therefore, it is important to discuss this treatment option with a healthcare professional and to understand the benefits and risks associated with HBOT.
More on Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy
