Glutamine: Health Benefits, Sources, Possible Side Effects
Glutamine is a popular supplement for any person who works out. In this article, we are to explain what is glutamine, what are its various functions, what are its health benefits, and from what food sources to obtain it. We will also examine the potential side effects and the differences between L-glutamine and d-glutamine.
What is Glutamine
Glutamine is an amino acid that belongs to the category of non-essential (i.e. our body can synthesize it from other amino acids found in the food we eat), it is part of proteins.
It is one of the most abundant amino acids in the human body, specifically the most abundant in muscle (60%) and also a source of nutrition for the brain.
It is the most abundant free amino acid in the body, making up 25% of the amino acids in extracellular fluid and over 60% of muscle. The major reservoir in glutamine is skeletal muscle. In a person weighing 70 kilograms, it is 50 grams of free glutamine and 240 grams of muscle.
When do glutamine stocks fall?
Glutamine stores seem to drop significantly when the body is under catabolic conditions. These occur after an operation or when there is a sudden loss of protein. One such example is multiple burns, where 50% of the body’s protein reserves can be lost.
For this reason, patients hospitalized for burns are given large amounts of glutamine intravenously, up to 60 g.
Glutamine stops protein loss and preserves nitrogen in the cells, as well as reducing the catabolic effects of cortisol and, slightly, myostatin, a protein that ‘blocks’ muscle growth.
Glutamine Food Sources
Glutamine Functions
Glutamine has many functions in the body, which include:
Glutamine Recommended Daily Allowance
The recommended daily allowance of L-Glutamine is 5 to 20 grams total divided before, during, and after training. Glutamine can be mixed with juice, water, and other supplements such as BCAA and protein powder. It is available in several refreshing flavors which will satisfy the most discerning!
✔️ TIP:
During the summer months, you can make glutamine granola bars by simply placing water with glutamine in the freezer in granola molds. This will also help with feeling like you’re eating something sweet during a hypothermic period!
Health Benefits of Glutamine
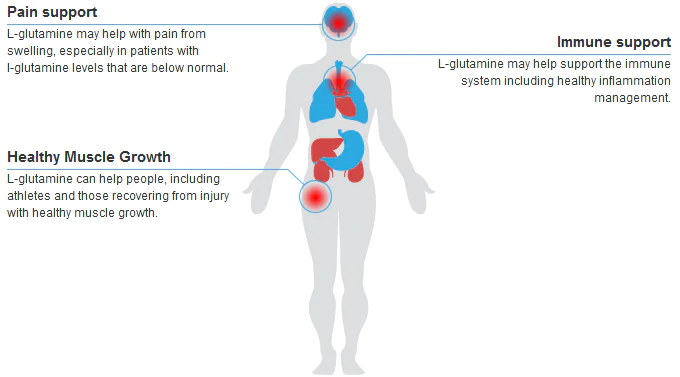
1. Helps in wound healing – Wounds, including those caused by surgery, often result in a loss of muscle mass. This is because the body uses glutamine to repair and rebuild tissue.
2. Reduces inflammation – Glutamine has anti-inflammatory properties and can help reduce swelling and pain associated with conditions such as arthritis.
3. Boosts immune function – Glutamine is a key player in the immune system, helping to fight off infection and disease.
4. Enhances exercise performance – Glutamine supplements have been shown to improve exercise performance by delaying fatigue and enhancing recovery.
5. Aids in weight loss – Glutamine can help boost metabolism and promote lean muscle mass, both of which can lead to weight loss.
6. May help treat digestive disorders – Glutamine is effective in treating various digestive disorders, such as Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis.
7. May protect brain health – Glutamine supplements have been shown to improve cognitive function and protect against age-related decline.
8. May help treat anxiety and depression – Glutamine has been shown to act as an antidepressant by increasing levels of serotonin and GABA in the brain.
9. May improve sleep quality – Glutamine supplements have been shown to improve sleep quality by reducing nighttime waking and restoring normal sleep patterns.
10. Aids in maintaining a healthy gut – Glutamine is essential for the health of the gut lining and can help treat various digestive disorders.
11. Reduces cravings – Glutamine supplements have been shown to reduce food cravings, especially for sugary and high-fat foods.
12. May help treat ADD and ADHD – Glutamine supplements have been shown to improve symptoms of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD).
13. Aids in detoxification – Glutamine helps the body remove toxins and waste products, making it an important part of any detoxification program.
14. May have anti-aging effects – Glutamine supplements have been shown to improve cell proliferation and help repair DNA damage.
Possible Side Effects of Glutamine
Glutamine is safe for most adults when taken orally in doses of up to 40 grams per day or when given intravenously in doses of up to 600 mg/kg body weight per day.
Side effects are generally mild and may include dizziness, heartburn, and stomach pain. Special precautions and warnings:
Children
Do not exceed doses up to 0.7 g/kg body weight per day or when administered intravenously in doses up to 400 mg/kg body weight per day. Always administer after consultation with the treating physician.
Pregnancy and breast-feeding
Glutamine is not known to be used during pregnancy and breastfeeding. It is advisable to avoid its use.
Avoid glutamine supplements in the following health conditions
Glutamine Supplements
Glutamine supplements are available in the form of powders, tablets, and capsules. They can be bought online or at health stores.
Some of the L-Glutamine supplements we recommend are:
L-Glutamine 100 Tablets By Puritan’s Pride: L-glutamine by Puritan’s Pride is cheap and contains 100 tablets, each containing 500 mg of L-glutamine. A great choice for anyone looking to supplement their diet with this essential amino acid.
Pure Encapsulations l-Glutamine Powder – 227 Grams: L-Glutamine from Pure Encapsulations comes in powder form and it is more expensive than L-Glutamine by Puritans Pride. It includes 73 servings per container and each serving yields around 3 grams of L-glutamine (3000 mg).
Microingredient’s L-Glutamine Powder, 1 Kilogram: If you’re looking for both quantity and quality, check out Microingredient’s L-glutamine powder. It comes with 1 kilogram (1000 grams) of L-glutamine per container and it is certified non-GMO, gluten-free, soy-free, and vegan. Take 1 teaspoon will yield you around 2 grams or 2000 mg. or roughly 2 teaspoons
Does glutamine have calories?
Reliable sources such as Layne Norton, claim that like all BCAAs, L-glutamine has up to 4 calories per gram (same as protein). However, counting calories from supplements is probably an exaggeration. Especially when there is consistency in taking them (consistency) it is best not to count calories.
L-glutamine and D-glutamine
Like many other amino acids, glutamine is found in two forms: L-glutamine and D-glutamine. This different name indicates a slightly different molecular arrangement; L-glutamine is the natural form found in foods and supplements, while D-glutamine is unimportant in living organisms.
Final Words
Glutamine supplements are generally safe when taken in the recommended dosage. However, side effects such as stomach pain, bloating, nausea, and vomiting have been reported. People with pre-existing medical conditions or who are taking medication should speak to a healthcare professional before taking glutamine supplements.
Dr. Berg’s Electrolyte Powder Formula
Dr. Berg’s Electrolyte Powder replenishes electrolytes and relieves muscular cramps. Dissolves easily and is ideal for promoting endurance, hydration, normal muscle function and energy. It’s also keto-friendly! Each dose includes 1000mg of potassium and absolutely no sugar, carbs, maltodextrin, or artificial additives.

