Is It OK to Consume Gelatin Daily? What Research Says.
Discover the potential benefits and risks of daily gelatin intake, and whether it's the right addition to your daily routine

- Daily gelatin consumption (5-15g) appears safe and beneficial for most people, offering potential advantages for joint health, skin elasticity, hair, gut function, and protein intake.
- Rich in glycine and proline, gelatin may also support sleep quality, blood sugar regulation, and bone health.
- However, choose high-quality sources to avoid heavy metal contamination, start with small amounts to prevent digestive discomfort, and consult a healthcare provider if you have allergies to animal products or medical conditions.
- Not a miracle supplement, but a potentially valuable addition to a balanced diet with benefits that develop gradually over time.
I recently learned something that surprised me during a hospital visit. The reason they serve jelly to patients isn’t just because it’s easy to eat – it’s actually packed with protein (and I always cringed whenever I saw jelly in a patients tray).
After confirming this with a nurse, I started noticing gelatin everywhere – in health videos, nutrition blogs, fitness magazines. I bought pure bovine gelatin from the supermarket and began adding one sachet to my daily protein shake. But then a question hit me: Is it OK to consume gelatin daily?
While gelatin offers several potential health benefits from joint support to improved skin health, it’s important to understand both the advantages and potential drawbacks before making it part of your everyday routine. In this article, we’ll explore what exactly, gelatin benefits, potential drawbacks and how to consume it.
What Exactly Is Gelatin?

Gelatin is a protein derived from collagen found in animal bones, skin, and connective tissues. It’s produced through a process called partial hydrolysis, where collagen is broken down by boiling animal tissues in water and treating them with acids or bases. This process breaks the molecular bonds between collagen strands, resulting in gelatin.
You’ll find gelatin available in several forms:
- Powdered gelatin (most common)
- Gelatin sheets (often used in professional cooking)
- Gelatin capsules (as dietary supplements)
Gelatin Nutrition Information (per 100g):
| Nutrient | Amount |
|---|---|
| Energy | 1555 kJ / 375 kcal |
| Fat | 10 g |
| – of which saturates | 0 g |
| Carbohydrates | 0 g |
| – of which sugars | 0 g |
| Protein (min.) | 86 g |
| Salt | 0.075 g |
How gelatin is made?
Now, instead of me explaining the whole process, why you don’t watch this 6 minutes video that’ll take you through the whole process.
But, if you want the TL;DR, note that Gelatin is made from animal collagen, typically from cow or pig tissues. The process involves cleaning the raw materials, pre-treating them with acid or alkaline solutions, extracting the collagen through hot water, filtering the mixture, concentrating it, sterilizing, and finally drying it into sheets, powder, or granules.
Daily Gelatin Consumption Benefits
People consume gelatin for various reasons. Including joint pain relief, improving skin appearance, supporting gut health, and as a protein source. I personally, do it because.. all the before mentioned reasons.
But does the evidence support these uses when taken daily? Let’s dig deeper.
1. Supports Joint Health
Gelatin contains high amounts of amino acids that serve as building blocks for cartilage – specifically glycine, proline, and hydroxyproline. These amino acids essentially provide the raw materials your body needs to repair and maintain cartilage tissue. When you consume gelatin regularly, you’re giving your body a steady supply of these building blocks.
Research suggests it may reduce joint pain and stiffness, especially in osteoarthritis.
- For example, a 1998 study at Ball State University found athletes with knee pain had less pain after consuming a gelatin supplement.
- Another study from UC Davis showed gelatin with exercise helped build ligaments and tendons. The mechanism? These amino acids support collagen synthesis, repairing joint tissues.
- Another study published in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition showed that gelatin supplementation combined with vitamin C improved collagen synthesis in the body. (Ed. note: Collagen is well-known for its role in relieving joint pain).
2. Good for Skin, Hair, and Nails
Collagen = the primary structural protein in skin that provides elasticity and hydration.
Collagen keeps skin elastic and hydrated, and as we age, we lose it, leading to wrinkles and sagging skin. Gelatin, rich in collagen peptides, may stimulate the body’s collagen production, potentially improving skin appearance.
Some studies exists that connect gelatin with better skin health:
- This study found that gelatin from Amur sturgeon swim bladder, rich in collagen peptides, improved skin aging in rats. After 12 months, it increased skin thickness (18.45%) and collagen density (22.17%), reduced oxidative stress, and boosted antioxidants. Results suggest it could be a promising anti-aging supplement.
- Another study found that gelatin from tuna skin, especially acid-extracted, protected skin cells from UV damage. Its peptides (under 3.5 kDa) showed strong antioxidant effects, suggesting potential for anti-aging skincare.
Many users report stronger nails and healthier hair after regular gelatin consumption, though these benefits are primarily anecdotal. The scientific research specifically on hair and nail benefits remains limited.
Some studies that are related to gelatin and hair growth are:
- A 2003 study published in the journal Biomaterials found that slow-release gelatin hydrogels containing growth factors (like FGF or HGF) boosted mice hair follicle growth, increasing hair shaft length without affecting skin thickness. (30 words)
- A 2004 research published in the journal Tissue Engineering found that slow-release gelatin hydrogels with bFGF boosted mice hair growth, increasing follicle size and hair length, especially during active growth phases. (30 words)
- Finally, a new 2025 study created a special gel with tiny gelatin-coated bubbles (called transferosomes) to deliver hair loss medicine (tofacitinib) straight to hair roots. When tested on patients with stubborn bald spots, 7 out of 7 saw hair regrow within 3 months – some up to 80% improvement! The gelatin coating helps the medicine go exactly where needed (hair roots) without affecting other areas.
(Ed. note: Most clinical studies have been conducted using hydrolyzed collagen rather than regular gelatin, which has slightly different properties but similar amino acid profiles.)
3. Gut Health and Digestion
Gelatin may support gut health in several ways.
It contains glutamic acid, which can be converted in the body to glutamine – an amino acid that helps maintain the integrity of the intestinal lining.
Dr. Sarah Ballantyne, author of “The Paleo Approach,” explains that “gelatin can help heal the gut lining and reduce intestinal inflammation.”
Dr. Axe notes it strengthens the gut lining, lowering inflammation, and WebMD mentions it builds a protective mucus lining, with early rat studies showing protection, though human evidence is limited.
Some research suggests that the glycine in gelatin may protect the stomach lining from damage and support digestive enzyme production.
“But doesn’t gelatin cause digestive issues for some people?”
Good question!
Some individuals do report mild digestive discomfort when first adding gelatin to their diet. This typically includes bloating or gas, which usually subsides as the body adjusts.
4. Source of Protein & Important Amino Acids
With approximately 6 grams of protein per tablespoon, gelatin provides a decent protein boost. However, it’s worth noting that gelatin is an incomplete protein – it lacks tryptophan, an essential amino acid.
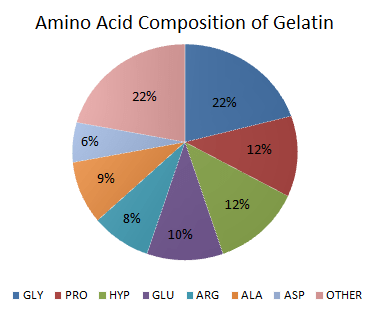
What makes gelatin unique is its high concentration of glycine (around 27%) and proline (15%) – amino acids often lacking in modern diets focused on muscle meats. These amino acids serve important functions:
- Glycine supports detoxification processes in the liver
- Glycine may improve sleep quality
- Proline contributes to collagen formation
A 2015 study found that glycine supplementation improved sleep quality and reduced daytime sleepiness in participants experiencing sleep problems.
5. Blood Sugar Regulation
Some research suggests gelatin may help with blood sugar management. The glycine in gelatin appears to support insulin response and glucose control.
A study published by the University of Alabama in Birmingham found that glycine supplementation improved insulin sensitivity in some individuals with type 2 diabetes. Since gelatin is rich in glycine, it might contribute to better glycemic control when consumed regularly.
6. Bone Health Support
Gelatin contains lysine, an amino acid that helps the body absorb calcium more effectively. This combination of improved calcium absorption and the amino acids needed for collagen formation may contribute to better bone density over time.
A 2009 study published in the journal Bone found that giving cod bone gelatin to rats with bone loss (similar to menopause in women) helped protect their bones. Rats receiving 3g/kg of gelatin daily for 90 days showed:
- 30% better bone structure
- Lower inflammation
- Reduced bone breakdown markers
The gelatin worked by balancing bone-regulating proteins and calming bone-damaging inflammation. This suggests fish gelatin could help prevent osteoporosis.
7. Appetite Regulation and Weight Management
Protein is known for its satiating effects, and gelatin is no exception. Some people report feeling fuller for longer after consuming gelatin-rich foods or supplements.
Plus, a small study in the The Journal of Nutrition found that gelatin increased satiety hormones compared to other proteins, potentially helping to reduce overall calorie intake throughout the day.
8. Liver Detoxification Support
The glycine abundant in gelatin plays an important role in liver detoxification pathways. Your liver uses glycine to help remove toxins from your body, and some research indicates that increasing glycine intake may support overall liver function. [1] [2]
Dr. Chris Masterjohn, a nutritional science researcher, notes that “glycine is required for phase 2 detoxification in the liver, which helps clear various environmental toxins.”
9. Better Sleep Quality
Glycine has been studied for its effects on sleep quality. I’ve found some scientific studies that support this claim. For example:
- This study found that glycine helps rats fall asleep faster and stay in deep sleep longer by acting on brain receptors (NMDA) in the sleep-control center (SCN). Glycine also lowered body temperature, which helps with sleep. When researchers blocked these receptors, glycine’s sleep benefits disappeared. This explains how glycine promotes better sleep naturally.
- In this study, people with poor sleep took 3g of glycine before bed. They fell asleep faster, had deeper sleep, and felt more refreshed the next day—without grogginess. Brain tests confirmed better sleep quality, and they performed better on memory tasks. Unlike sleeping pills, glycine improved sleep naturally without disrupting sleep stages. (58 words)
Since gelatin is one of the richest dietary sources of glycine, regular consumption might contribute to improved sleep patterns.
10. Heart Health Benefits
Some preliminary research suggests gelatin may support cardiovascular health. The amino acids in gelatin may help maintain the integrity of blood vessel walls and potentially improve circulation.
A study published in the British Journal of nutrition ound that collagen supplements help heart health by lowering bad cholesterol (LDL), reducing blood pressure, and improving body composition (less fat, more muscle) without affecting blood sugar.
11. Potential Anti-inflammatory Effects
The glycine in gelatin has demonstrated anti-inflammatory properties in several studies. A research review in the Journal Nutrients suggested that glycine supplementation might help reduce inflammation and oxidative stress in various tissues throughout the body. For those dealing with chronic inflammatory conditions, this could be an additional benefit of regular gelatin consumption.
Potential Drawbacks and Side Effects
Despite its benefits, daily gelatin consumption isn’t without potential issues:
- Allergies: Though uncommon, some people may experience allergic reactions to gelatin. Symptoms can range from hives to more serious reactions. If you have known allergies to meat products, approach gelatin with caution.
- Digestive Issues: Some users report bloating, heartburn, or an unpleasant feeling of fullness. Starting with small amounts and gradually increasing can help minimize these effects.
- Heavy Metal Concerns: Gelatin is derived from animal tissues, which may contain environmental contaminants. A 2013 analysis published in Food Additives & Contaminants found varying levels of heavy metals in different gelatin products. Choosing products from reputable companies that test for contaminants is key (more on that later).
- Medication Interactions: Gelatin might affect the absorption of certain medications. [3]
Dosage and How to Consume Gelatin
Most research suggests a daily intake of 5-15 grams of gelatin can provide potential benefits without causing side effects. This translates to roughly 1 sachet of powdered gelatin.

Ways to add gelatin into your daily routine:
- Add to morning coffee or tea
- Mix into smoothies (won’t affect taste) – (Gelatin Smoothie Recipe)
- Make homemade gelatin gummies with fruit juice
- Add to soups and broths for extra protein
- Use in homemade desserts.
Gelatine – Instructions for Dissolving
General Instructions:
- Always add the gelatin into the liquid—not the other way around.
- Empty the gelatin into the cup with very hot liquid and stir quickly.
- If it doesn’t fully dissolve (because the liquid cooled), you can finish the process using a bain-marie (hot water bath).
- Do not let the gelatin mixture boil.
Step-by-Step Instructions:
- Half cup of hot water (or as required by your recipe).
- Pour the gelatin into the hot water.
- Whisk quickly until gelatin is completely dissolved.
- The gelatin mixture is ready to use.

Gelatin differs from collagen hydrolysate (collagen peptides) in that gelatin forms a gel in cold liquids, while collagen peptides dissolve completely. For hot beverages or recipes where you don’t want gelling, collagen peptides might be preferable.
Gelatin Brands with Low Heavy Metal Contamination
Finding gelatin products specifically tested for heavy metal content can be challenging, as not all manufacturers publish comprehensive testing results. However, here are three reputable gelatin brands that prioritize quality control and testing for contaminants:
Great Lakes Gelatin is frequently recommended by nutritional professionals for its quality control standards. The company sources its gelatin from grass-fed, pasture-raised cattle from Argentina and Brazil. Their products undergo third-party testing and the company claims to test for heavy metals including lead, arsenic, cadmium, and mercury.
Their Collagen Hydrolysate (the green canister) and traditional Beef Gelatin (the red canister) are their most popular products. They provide certificates of analysis upon request, which can give you specific information about testing results.
Vital Proteins has built a strong reputation for quality control and sourcing standards. Their beef gelatin comes from grass-fed, pasture-raised bovine hides from Brazil. The company states that they regularly test their products for heavy metals and other contaminants.
Vital Proteins publishes some testing information on their website and emphasizes their commitment to third-party testing. Their Beef Gelatin product is unflavored and can be easily incorporated into various recipes.
NOW Foods has established itself as a company with rigorous quality testing protocols. They operate an in-house analytical laboratory and conduct tests for heavy metals, microbial contaminants, and adulterants across their product line.
Their beef gelatin is kosher and tested for purity. NOW Foods is also transparent about their quality assurance practices and publishes information about their testing protocols on their website.
- Look for companies that offer certificates of analysis upon request – this shows transparency about testing results.
- Choose products from companies that source from grass-fed animals when possible, as these may have lower exposure to environmental contaminants.
- Contact manufacturers directly with specific questions about their heavy metal testing protocols if this information isn’t readily available on their websites.
- Consider products with third-party certifications such as NSF, USP, or other independent quality verifications
- Read user reviews focusing specifically on product quality rather than just taste or effectiveness
Remember that even with these recommendations, no product can guarantee zero contamination, as trace amounts of heavy metals occur naturally in soil and water. The goal is to minimize exposure by choosing companies with stringent quality control.
If you have specific health concerns about heavy metal exposure, consulting with a healthcare provider knowledgeable about nutritional supplements would be advisable before beginning daily gelatin consumption.
Bottom Line: Is Daily Consumption Right for You?
After reviewing the available research on gelatin consumption, here’s what we know: For most healthy adults without specific allergies or medical conditions, moderate daily gelatin consumption (5-15g) appears to be safe and potentially beneficial.
Who might benefit most from daily gelatin:
- Those with joint discomfort or osteoarthritis
- People looking to support skin health
- Individuals with certain digestive issues
- Those seeking to increase specific amino acids in their diet
Who should exercise caution:
- People with known allergies to animal products
- Those on multiple medications
- Individuals with kidney or liver conditions
- Pregnant or breastfeeding women (due to limited research)
The bottom line? If you can consume gelatin without allergic reactions, daily intake within recommended amounts is generally considered safe. However, as with any supplement, it’s smart to check with your healthcare provider before making it a daily habit, especially if you have existing health conditions.
For most people, gelatin can be a beneficial addition to a balanced diet – just don’t expect miracle results overnight. The potential benefits tend to develop gradually with consistent use over time.



