Citrullus Ecirrhosus (Namib Tsamma): Benefits, Uses, Side Effects and Potential Interactions
Discover Citrullus ecirrhosus its remarkable benefits, uses, and potential side effects.
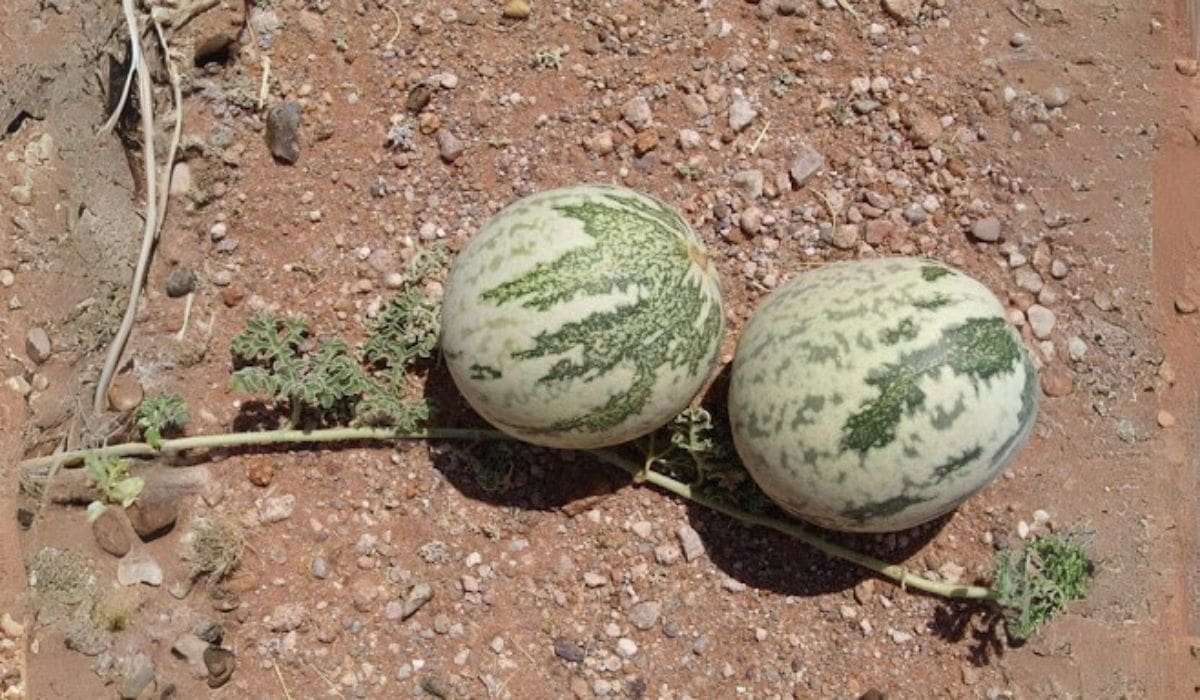

Citrullus Ecirrhosus, also known as Namib Tsamma, Wild Melon or Tsamma Melon, is a nutrient-rich melon indigenous to the Namib Desert. Historically significant, it has served as a crucial hydration source and food for indigenous populations, particularly the San.
Rich in water, vitamins, and antioxidants, it promotes digestive health and exhibits anti-inflammatory effects. While typically safe when consumed properly, raw or bitter melons may cause toxicity, necessitating cooking.
Limited interactions with medications have been noted. In this article we’re going to explore Citrullus Ecirrhosus benefits as well as its Uses and potential side effects and interactions with medications and other substances.
What is Citrullus Ecirrhosus?
Citrullus ecirrhosus, also known as Namib tsamma, is a type of vine that grows in deserts and is part of the Cucurbitaceae family, which includes melons and gourds.
It has a hard, white inside that tastes bitter and has yellow flowers. This vine is related to the bitter melon and is found mainly in dry areas of South Africa and Namibia, especially in the Namib Desert.

Citrullus ecirrhosus can survive tough conditions by getting water from deep underground and using morning fog to protect it from the harsh sun.
This plant has been important historically, with signs showing it was grown in the Nile Valley around 2000 BC. It is one of the ancestors of today’s watermelons and is adapted to arid environments, allowing it to thrive in challenging habitats. [1]

The San tribes used the fruit to stay hydrated during dry winter months in the Kalahari Desert, and they also stored the fruits for a long time.
They used the seeds to make oil for their skin, showing how useful this plant was for both food and taking care of their bodies. [2]
Citrullus Ecirrhosus nutrition profile
An analysis of the nutritional content of Citrullus Ecirrhosus shows that it has a lot of water, more than 90%, in the fruit part, which makes it great for staying hydrated.
This is especially helpful in dry places, providing a source of water for animals and people. The fruit also has important nutrients like Vitamin C, pectin, and ascorbic acid, which are good for health.
The seeds of Citrullus ecirrhosus also have a lot of nutrients.

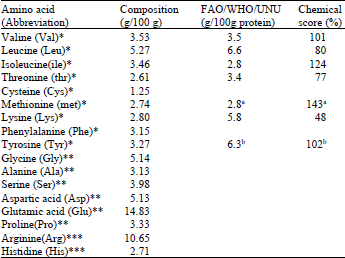
They have about 35% protein and around 50% oil, similar to pumpkin seed oil, making them a good source of energy and nutrients.
The seeds also have about 5% dietary fiber, which helps with digestion. They also contain vitamins and minerals, including riboflavin.
The table below shows the nutritional makeup of both the fruit and seeds:
| Component | Fruit Pulp | Seeds |
|---|---|---|
| Water Content | >90% | Variable |
| Protein Content | Negligible | ~35% |
| Oil Content | Negligible | ~50% |
| Dietary Fiber | Negligible | ~5% |
| Vitamins & Minerals | Vitamin C, trace elements | Riboflavin, Vitamin C |
Citrullus Ecirrhosus Health Benefits
Citrullus ecirrhosus offers many health benefits backed by research and experts.
Its high water content and essential vitamins help with hydration and maintaining electrolyte balance, especially in dry areas. This makes the fruit a vital water source for both livestock and humans during droughts. The fruit’s 90% water content is particularly important for animals and people living in deserts during dry seasons.
Additionally, the fruit has strong antioxidant properties, supports digestive health, and has anti-inflammatory effects, making it useful for both nutritional and medicinal purposes.

1. Antioxidant Properties
Even though there hasn’t been a lot of research on Citrullus Ecirrhosus, its similarity to watermelon suggests it might have similar health benefits.
Watermelon contains lycopene, which is known for its antioxidant capabilities. Antioxidants help protect the body against damage and can lower the risk of diseases like cancer and diabetes, and help with high blood pressure.
Plus, this species is native to Southern Africa, where it has adapted to thrive in arid environments, further emphasizing its resilience and potential health benefits.
2. Hydration and Electrolyte Balance
Staying hydrated is super important for our health, especially in dry places where water is hard to find. The Namib tsamma melon is a real life-saver in these situations because it’s over 90% water!
This not only helps keep desert habitats hydrated but also keeps their body’s electrolytes balanced, thanks to vitamin C and tiny amounts of minerals in its pulp.
Plus, the melon has antioxidant properties that may help combat oxidative stress, making it even more beneficial for our health.

3. Reduces Arterial Stiffness
Citrullus ecirrhosus has been found to further benefit cardiovascular health. According to a study published in the journal Nutrients, consuming wild watermelon-extracted juice can significantly reduce arterial stiffness in the lower limbs.
The study observed that this juice boosts the production of nitric oxide, which helps relax blood vessels, improve blood flow, and reduce arterial stiffness.
Twelve healthy young women participated in a randomized, double-blind crossover pilot study where they drank either the watermelon juice or a placebo.
Results showed that those who consumed the juice experienced better blood flow and less stiffness in their arteries compared to the placebo group.
This suggests that wild watermelon could be a valuable natural remedy for improving vascular health, especially in dry environments where it naturally grow
What other uses it has?
Citrullus ecirrhosus, has many uses beyond just being food. It helps the environment, can be used in cooking, and has practical applications, especially in dry areas.
- Helping the Environment: This melon is a crucial water source for animals in the desert, providing both hydration and food, which helps sustain life in areas with few resources. Additionally, its ability to grow in diverse habitats supports local wildlife by providing hydration.
- Cooking Uses: The melon’s flesh can be cooked to enhance its flavor and can be used in various dishes. Without cokking it’s tasteless. The young leaves and flowers can also be eaten, and the pulp, which is not bitter and high in pectin, is perfect for making jam.
- Practical Uses: The dried skin of the melon can be used to start fires, an essential skill for survival. The flesh and skin can also provide hydration, making it very valuable in desert areas.
- Agricultural Research: Studying Citrullus ecirrhosus helps scientists develop pest-resistant watermelons by crossbreeding it with closely related plants, such as Citrullus lanatus. [3]
- Make a bowl: You can use its shell like a natural bowl to carry and prepare other foods, making meals more nutritious. The San people have used tsamma melons for a really long time, especially during hunts, proving how important they are for surviving in tough environments.
Citrullus Ecirrhosus Side Effects
Although Citrullus ecirrhosus doesn’t seem to have that many health benefits, it’s important to know about its possible side effects.
Citrullus ecirrhosus, which is closely related to Citrullus colocynthis, can cause various health issues, especially when consumed in large amounts. Studies have shown that extracts from these plants can lead to serious problems like stomach issues and changes in blood cells.
Here are some key side effects observed in research:
- Blood Cell Changes: Animals treated with these extracts showed significant changes in their red blood cell counts, hemoglobin levels, and white blood cells, indicating potential blood toxicity.
- Stomach Issues: High doses of Citrullus colocynthis extracts have been linked to severe diarrhea and stomach irritation.
- Embryo Survival: In pregnant mice, higher doses of Citrullus colocynthis led to more embryo deaths and fewer viable embryos, suggesting it could harm reproduction.
- Tissue Damage: Studies found damage to stomach tissues, including the loss of protective lining and inflammation, especially at higher doses.
While Citrullus ecirrhosus may have some health benefits, it’s important to be cautious about how much and how long you use it. More research is needed to fully understand its safety and potential uses.
Interactions
Right now, there aren’t any known problems between this plant and medicines or supplements, but not much research has been done.
The plant is part of the Cucurbitaceae family, which has some plants with chemicals that might affect how medicines work, but we don’t know if this plant does that too.
But, as mentioned, we don’t have enough information to know everything about how Citrullus ecirrhosus works inside the body. In the past, people used it more for food and water than as a supplement, so we don’t know much about how it might work with other supplements.
We need more research to really understand if this plant can cause problems when used with medicines or supplements. For now, if you are taking medicine or other supplements, you should ask a doctor before using Citrullus ecirrhosus, just to be safe.

How to Consume it?
The Tsamma melon, also known as Citrullus ecirrhosus, can be used in several ways.
- You can eat the juicy and vitamin-rich pulp directly to stay hydrated.
- The seeds can be roasted or boiled to extract oil, which helps protect your skin from sunburn.
- You can also chew the seeds to make a paste for smoother skin.
- Plus, the young leaves and flowers can be eaten as vegetables
- The flesh can be dried in the sun and added to stews and other dishes.
There isn’t a specific recommended amount for consuming the different parts of the Tsamma melon, as it depends on what you’re using it for, such as hydration or skincare. It’s important to only eat the non-bitter melons, as the bitter ones should only be used to extract seeds.
Since there isn’t much research on the nutritional value and potential toxicity of Citrullus ecirrhosus, it’s best to consume it in moderation.
What’s the difference between Citrullus Ecirrhosus and Citrullus Vulgaris?
Citrullus ecirrhosus and Citrullus vulgaris belong to the same plant genus, but they are quite different in how they grow, where they thrive, and how we use them.
Citrullus ecirrhosus is built to survive in tough, dry conditions. This plant is unusual because it doesn’t have tendrils, which are the curly, string-like structures that many plants use to climb or spread out. Its fruits are smaller, less juicy, and not something you’d typically find at the grocery store. However, it’s important for its drought resistance and is sometimes used in agricultural research to help make other crops hardier.
Citrullus vulgaris, on the other hand, is what we know as watermelon. It originated in Africa but is now grown worldwide. This plant has tendrils to help it spread, and it prefers rich, well-drained soils. The fruit is large, sweet, and juicy, making it a favorite for snacks, salads, and desserts. You’ll find watermelons in a variety of colors, including red, pink, yellow, and even white.
So, while they’re relatives, C. ecirrhosus is a survivor in the wild, and C. vulgaris is the tasty, cultivated star of picnics everywhere.
Where can You Buy Citrullus Ecirrhosus?
Finding Citrullus ecirrhosus can be tough because it’s not usually sold in regular stores. This herb mostly comes from Namibia and isn’t easy to get everywhere.
There’s a group called the Eudafano Women’s Co-operative that makes oil from the seeds of this plant, which might be one of the few places to get it.
Even though some African markets have things made from a similar plant, Citrullus lanatus, it’s hard to find Citrullus ecirrhosus online. Only a few websites that sell natural stuff might have it, but it’s not common.
Final Take
To sum up, Citrullus ecirrhosus is a hardy plant adapted to dry climates, with a history of use in traditional practices. Its high water content makes it useful in arid regions for hydration, but its nutritional benefits appear limited compared to other fruits. While it does contain Vitamin C and pectin, these are not present in amounts that significantly impact health based on current research.
The seed oil has some practical uses, such as keeping the skin moisturized, which has made it a niche ingredient in certain beauty products. However, claims about its benefits for sun protection and overall health are not strongly supported. The fruit and seeds can be used in food, but caution is necessary as some varieties are bitter, and improperly prepared seeds may be harmful due to their saponin content.
There’s little evidence supporting its use in medicine, including its supposed ability to combat parasites. More studies are needed to confirm these effects and to understand any potential risks, especially for those taking other medications.
The San/Bushmen have valued this plant for generations, emphasizing its cultural significance. Their knowledge reminds us of the importance of respecting and preserving traditional wisdom.
